Xenon Noble Gas Configuration
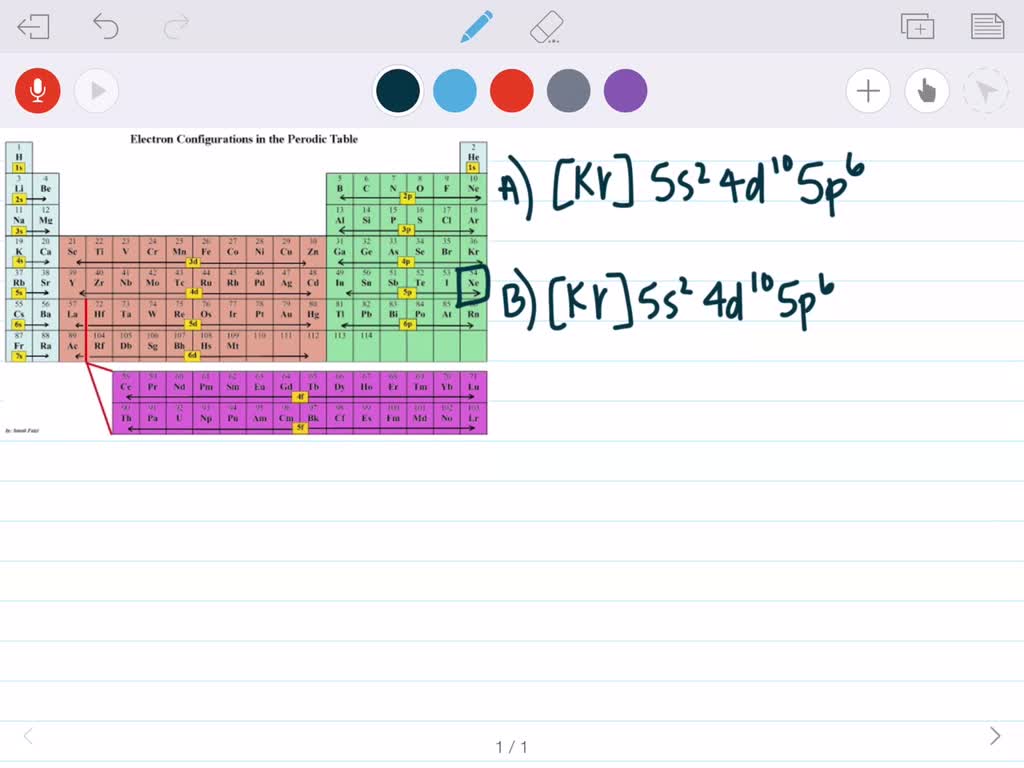
The noble gases are a group of elements in the periodic table that are characterized by their unreactive nature. Among these, Xenon (Xe) is a noble gas that has garnered significant attention due to its unique properties and applications. Understanding the noble gas configuration of Xenon is essential to grasp its chemical behavior and physical characteristics.
Introduction to Noble Gases
Noble gases are located in the far right column of the periodic table and include Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar), Krypton (Kr), Xenon (Xe), and Radon (Rn). These elements are known for their stability, which is attributed to their full outer energy level. This full outer shell makes it difficult for noble gases to react with other elements, as they do not readily gain, lose, or share electrons.
Electronic Configuration of Xenon
The electronic configuration of Xenon is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰ 4s² 4p⁶ 4d¹⁰ 5s² 5p⁶. This configuration indicates that Xenon has a full outer energy level, with all its subshells completely filled. The noble gas configuration is often denoted as [Kr] 5s² 5p⁶, where [Kr] represents the electronic configuration of Krypton, the noble gas preceding Xenon in the periodic table.
Physical Properties of Xenon
Xenon is a colorless, odorless, and heavy gas. It has a high atomic mass of approximately 131.29 u (unified atomic mass units) and a density of about 5.88 g/l at standard temperature and pressure. Xenon is also known for its high ionization energy, which is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in its ground state. This high ionization energy is a reflection of the stability of Xenon’s noble gas configuration.
Chemical Properties of Xenon
Despite being a noble gas, Xenon is not completely inert. Under certain conditions, such as high pressures and temperatures, Xenon can form compounds with other elements, particularly fluorine and oxygen. These compounds, known as xenon fluorides and xenon oxides, respectively, are highly reactive and have unique properties.
Applications of Xenon
Xenon has several applications due to its unique properties. It is used in:
- High-Intensity Lamps: Xenon is used in high-intensity lamps, such as xenon headlights in vehicles, due to its ability to produce a bright, white light when excited by an electric discharge.
- Anesthesia: Xenon is used as a general anesthetic due to its anesthetic properties and low toxicity.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Xenon is used in MRI machines as a contrast agent to produce detailed images of the lungs and other soft tissues.
- Space Exploration: Xenon is used as a propellant in ion thrusters for spacecraft due to its high atomic mass and the efficiency of ion propulsion systems.
Conclusion
Xenon’s noble gas configuration is a key factor in its chemical and physical properties. Its full outer energy level makes it highly stable, contributing to its unreactive nature. However, under specific conditions, Xenon can form compounds, showcasing its unique chemical behavior. The applications of Xenon are diverse, ranging from lighting and medical applications to advanced technologies in space exploration. Understanding the noble gas configuration of Xenon provides insights into its behavior and applications, making it an intriguing element in the periodic table.
What is the electronic configuration of Xenon?
+The electronic configuration of Xenon is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰ 4s² 4p⁶ 4d¹⁰ 5s² 5p⁶, which can also be represented as [Kr] 5s² 5p⁶, emphasizing its noble gas configuration.
Is Xenon completely inert?
+No, despite being a noble gas, Xenon is not completely inert. It can form compounds with elements like fluorine and oxygen under certain conditions, showcasing its ability to react under specific circumstances.
What are some applications of Xenon?
+Xenon has various applications, including its use in high-intensity lamps, as a general anesthetic, in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as a contrast agent, and in space exploration as a propellant in ion thrusters.
In conclusion, the noble gas configuration of Xenon plays a pivotal role in its properties and applications. Its unique characteristics make it a valuable element in various fields, from medicine and lighting to advanced space technology. The understanding and application of Xenon continue to evolve, further expanding its potential uses in science and technology.