What Causes Slough In Wounds? Healing Solutions
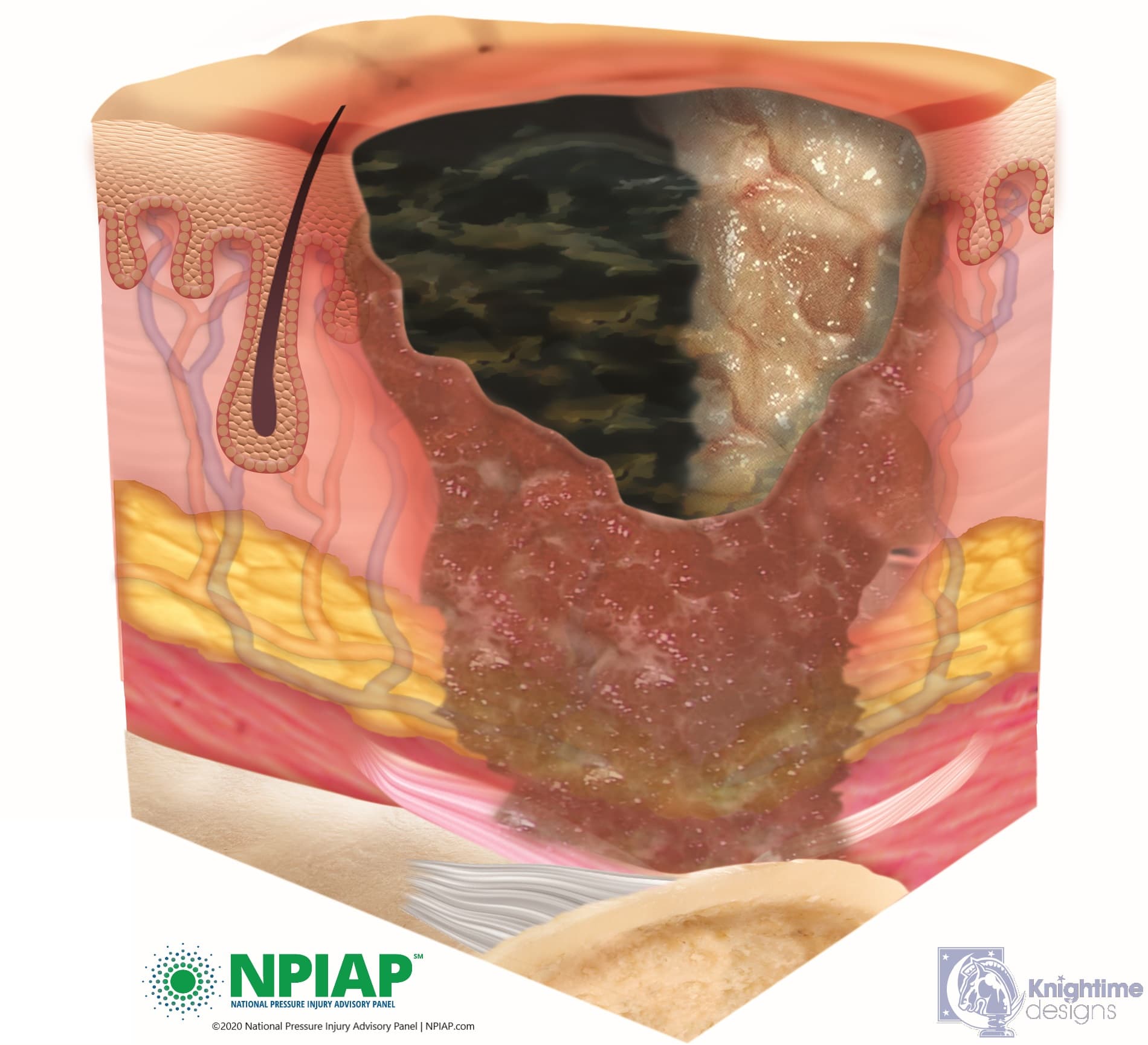
Slough in wounds is a complex and multifaceted issue that can significantly impede the healing process. To understand the causes of slough, it is essential to delve into the underlying biological processes that occur during wound healing. When a wound is sustained, the body’s initial response is to initiate the inflammatory phase, characterized by the activation of immune cells, the release of cytokines, and the formation of a provisional matrix. This phase is crucial for clearing debris, bacteria, and damaged tissue from the wound site.
However, in some cases, the inflammatory response can become dysregulated, leading to the accumulation of slough. Slough, also known as necrotic tissue, is composed of dead cells, fibrin, and other debris that can obstruct the wound bed, preventing the formation of granulation tissue and the subsequent phases of wound healing. Several factors can contribute to the development of slough, including:
- Inadequate debridement: Failure to remove dead tissue, bacteria, and other foreign material from the wound site can lead to the accumulation of slough.
- Infection: Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections can cause tissue damage, leading to the formation of slough.
- Poor circulation: Inadequate blood flow can impede the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the wound site, causing tissue damage and slough formation.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Inadequate nutrition, particularly protein, vitamin, and mineral deficiencies, can impair wound healing and contribute to slough formation.
- Chronic diseases: Conditions such as diabetes, vascular disease, and immunodeficiency can compromise wound healing, increasing the risk of slough formation.
To address slough in wounds, healthcare professionals employ various healing solutions, including:
Debridement Techniques
Debridement is the removal of dead tissue, bacteria, and other debris from the wound site. There are several debridement techniques, including:
- Surgical debridement: The use of surgical instruments to remove dead tissue and debris.
- Autolytic debridement: The use of dressings that promote self-cleansing of the wound, allowing the body to naturally remove dead tissue.
- Enzymatic debridement: The use of enzymes to break down dead tissue and debris.
Topical Therapies
Topical therapies can help promote wound healing and reduce slough formation. These include:
- Growth factor therapies: The application of growth factors, such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), to stimulate cellular proliferation and tissue repair.
- Antimicrobial therapies: The use of antimicrobial agents, such as silver-based dressings, to reduce bacterial colonization and infection.
- Moisture-retentive dressings: The use of dressings that maintain a moist environment, promoting autolytic debridement and tissue repair.
Systemic Therapies
Systemic therapies can help address underlying conditions that contribute to slough formation. These include:
- Antibiotics: The use of antibiotics to treat underlying infections.
- Nutritional supplements: The administration of nutritional supplements, such as protein, vitamins, and minerals, to support wound healing.
- Wound care education: Educating patients on proper wound care and management to prevent complications and promote healing.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are being developed to address slough in wounds, including:
- Bioengineered dressings: The use of bioengineered dressings that promote tissue repair and regeneration.
- Stem cell therapies: The use of stem cells to promote tissue repair and regeneration.
- Negative pressure wound therapy: The use of negative pressure to promote wound healing and reduce slough formation.
What is the most effective way to remove slough from a wound?
+The most effective way to remove slough from a wound depends on the individual patient and the wound characteristics. However, surgical debridement is often considered the gold standard for removing dead tissue and debris.
How can I prevent slough from forming in a wound?
+Preventing slough formation requires a comprehensive approach to wound care, including proper debridement, infection control, and nutritional support. Additionally, maintaining a moist environment and using topical therapies can help promote wound healing and reduce slough formation.
What are the consequences of untreated slough in wounds?
+Untreated slough in wounds can lead to complications such as infection, amputation, and even death. Prompt and effective management of slough is essential to promote wound healing and prevent long-term consequences.
In conclusion, slough in wounds is a complex issue that requires a comprehensive approach to management. By understanding the underlying causes of slough and employing a range of healing solutions, healthcare professionals can promote wound healing and improve patient outcomes. Further research is needed to develop innovative therapies and technologies to address slough in wounds, ultimately improving patient care and quality of life.
| Healing Solution | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical Debridement | Effective removal of dead tissue and debris | Potential for bleeding and infection |
| Autolytic Debridement | Promotes self-cleansing of the wound | May be slow and require frequent dressing changes |
| Growth Factor Therapies | Stimulates cellular proliferation and tissue repair | May be expensive and require repeated applications |

As the field of wound care continues to evolve, it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest research and technologies to provide optimal care for patients with slough in wounds. By working together, healthcare professionals can develop innovative solutions to address this complex issue and improve patient outcomes.
