Venous Duplex Scan
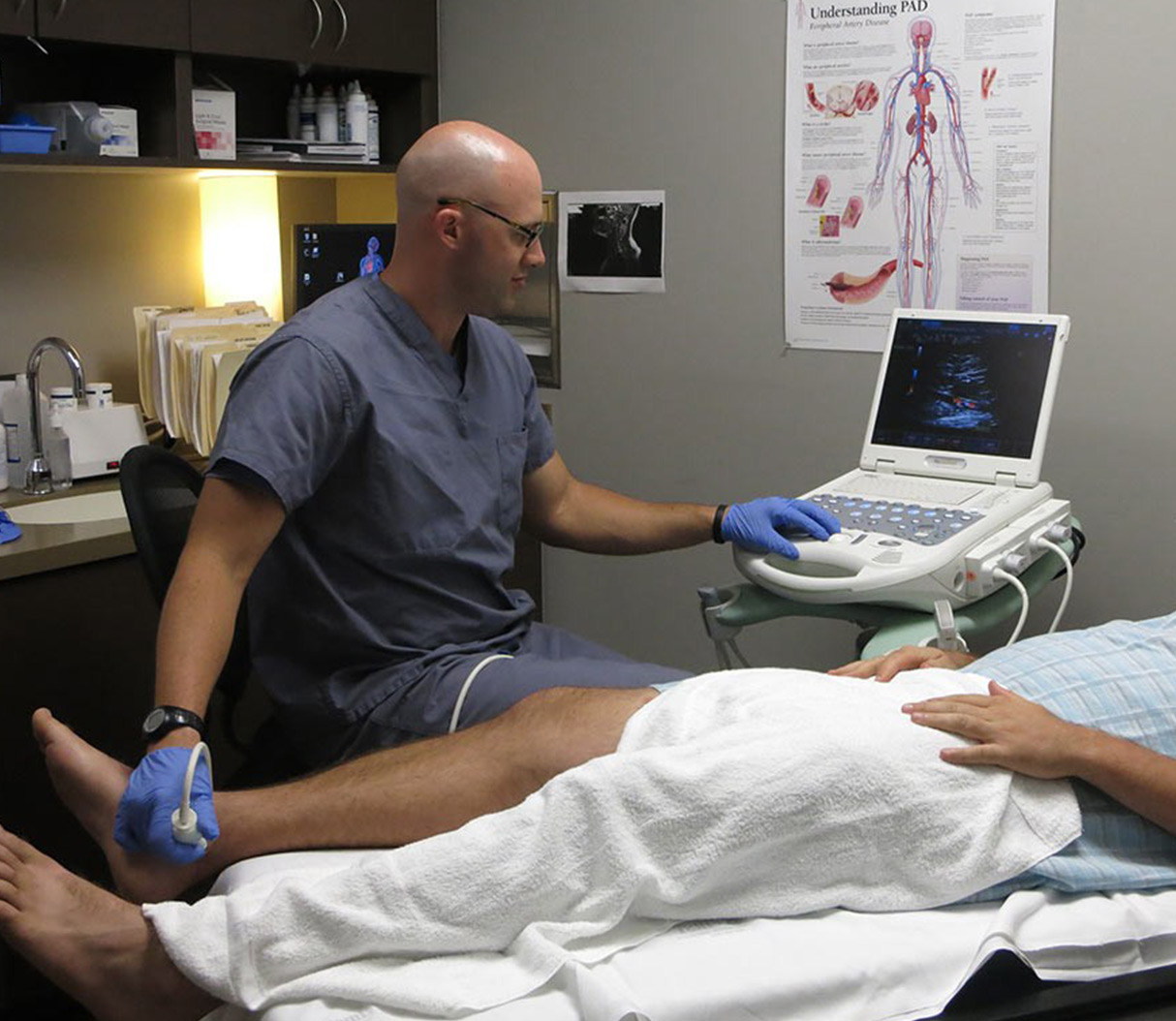
A venous duplex scan is a non-invasive medical imaging test used to evaluate the blood flow through the veins, typically in the legs. This diagnostic tool combines two types of ultrasound: Doppler ultrasound and conventional ultrasound. The Doppler component assesses the blood flow, while the conventional ultrasound provides images of the vein structures.
The primary purpose of a venous duplex scan is to diagnose conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), varicose veins, and venous insufficiency. DVT is a serious condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that can be painful and are often visible under the skin. Venous insufficiency refers to the inefficiency of the venous system in returning blood from the legs back to the heart, leading to symptoms like swelling, pain, and skin changes.
How the Test is Performed
The procedure for a venous duplex scan is straightforward and relatively quick, typically taking about 30 minutes to an hour to complete. Here’s what you can expect:
- Preparation: You will be asked to remove any clothing or jewelry that might interfere with the ultrasound waves. You may also be asked to change into a gown.
- Positioning: You will lie on an examination table, usually on your back, though you may be asked to turn onto your side or sit up at certain points during the test.
- Ultrasound Gel Application: The technician will apply a clear, water-based gel to the area being examined. This gel helps the ultrasound waves to penetrate more easily.
- Probe Placement: The technician will then place a handheld device called a transducer against your skin. The transducer sends and receives the ultrasound waves, converting them into electrical signals that are then displayed as images on a monitor.
- Data Collection: The technician will move the transducer along the length of the vein, taking images and assessing blood flow. For the Doppler part of the exam, you may hear a “whooshing” sound, which represents the flow of blood through the veins.
- Compression: At certain points, the technician may apply gentle pressure with the transducer to check for the presence of blood clots. In a normal vein, the blood flow should increase when the vein is compressed and decrease when it is released. If a clot is present, the vein may not compress properly.
- Conclusion: After completing the examination, the technician will wipe off the gel, and you can resume your normal activities immediately.
Understanding the Results
The results of a venous duplex scan can help your doctor diagnose a variety of venous conditions and guide treatment decisions. Here are some outcomes you might encounter:
- Normal Results: The test shows normal blood flow through the veins, and no signs of clotting, varicose veins, or insufficiency are detected.
- Abnormal Results: The test may indicate the presence of a blood clot (DVT), varicose veins, or other problems with venous blood flow. In such cases, your doctor may prescribe medication, recommend lifestyle changes, or discuss surgical options.
- Inconclusive Results: Sometimes, the test may not provide a clear diagnosis, in which case additional testing may be needed.
Benefits and Risks
The venous duplex scan offers several benefits, including non-invasiveness, lack of radiation exposure, and the ability to provide detailed images of the veins in real-time. However, as with any medical test, there are potential risks and considerations:
- Benefits: It’s a painless, non-invasive procedure that can be performed in a clinical setting. It does not use ionizing radiation, making it safe for pregnant women and individuals who require repeated imaging.
- Risks: While generally safe, the test may cause some discomfort due to pressure from the transducer. In rare cases, the ultrasound gel may cause skin irritation.
Conclusion
A venous duplex scan is a valuable diagnostic tool for evaluating venous conditions. Its ability to provide detailed images of vein structure and assess blood flow makes it an indispensable resource for clinicians when diagnosing and managing conditions like DVT, varicose veins, and venous insufficiency. Given its safety profile, ease of use, and effectiveness, the venous duplex scan plays a critical role in vascular medicine, helping to improve patient outcomes by facilitating early diagnosis and intervention.
When considering a venous duplex scan, it’s essential to discuss any concerns or questions you have with your healthcare provider. This includes understanding the reasons for the test, what to expect during the procedure, and how the results will be used to guide your care.
FAQ Section
What is the purpose of a venous duplex scan?
+The primary purpose of a venous duplex scan is to evaluate blood flow through the veins, typically to diagnose conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), varicose veins, and venous insufficiency.
Is a venous duplex scan painful?
+No, a venous duplex scan is generally not painful. You may experience some discomfort due to the pressure from the transducer, but the procedure is non-invasive and does not require any needles or injections.
How long does a venous duplex scan take?
+A venous duplex scan typically takes about 30 minutes to an hour to complete, depending on the complexity of the examination and the technician's findings.
What are the benefits of a venous duplex scan?
+The benefits include its non-invasive nature, lack of radiation exposure, and the ability to provide real-time images of the veins. This makes it a safe and effective diagnostic tool for a variety of venous conditions.
Can a venous duplex scan be used during pregnancy?
+Yes, a venous duplex scan is safe for use during pregnancy. It does not involve any radiation, making it a preferred diagnostic method for pregnant women when venous conditions need to be evaluated.
By understanding what a venous duplex scan entails and what it can diagnose, individuals can better navigate their healthcare journey, especially when dealing with venous conditions. This comprehensive diagnostic approach not only aids in the detection of venous issues but also plays a critical role in the prevention of complications and the improvement of treatment outcomes.
