Spinal Fluid Protein High
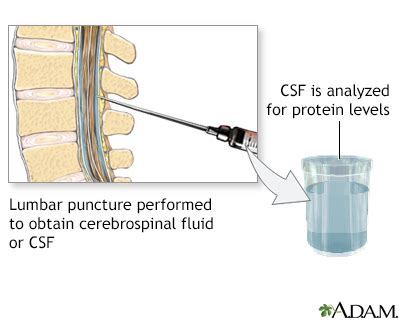
The presence of high levels of protein in the spinal fluid, also known as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), can be an indicator of various neurological conditions. The CSF is a clear, colorless fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, providing cushioning, support, and immune protection. It is produced by the choroid plexus in the ventricles of the brain and circulates through the subarachnoid space, which is the area between the brain and the skull, and the spinal canal.
Under normal conditions, the CSF contains a small amount of protein, typically less than 50 milligrams per 100 milliliters. However, when the protein level in the CSF exceeds this normal range, it can signify the presence of an underlying neurological disorder. Elevated CSF protein levels can result from various conditions, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and injuries that affect the central nervous system.
Causes of Elevated CSF Protein
Several factors can lead to high protein levels in the spinal fluid. Some of the most common causes include:
- Meningitis: This is an infection of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known as the meninges. Meningitis can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms, and it often leads to an increase in protein levels in the CSF.
- Encephalitis: This is an inflammation of the brain tissue, usually caused by a viral infection. Encephalitis can also result in elevated protein levels in the CSF.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome: This is a rare autoimmune disorder that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the nerves, leading to muscle weakness and paralysis. One of the characteristic features of Guillain-Barré Syndrome is an increase in protein levels in the CSF.
- Multiple Sclerosis: This is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, causing demyelination, inflammation, and a range of neurological symptoms. Elevated CSF protein levels can be a feature of multiple sclerosis.
- Spinal Cord Injury: Trauma to the spinal cord can cause an increase in protein levels in the CSF due to the disruption of the blood-spinal cord barrier.
Diagnosis and Treatment
To diagnose the cause of elevated CSF protein levels, a healthcare professional will typically perform a lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, to collect a sample of the spinal fluid. The CSF sample will then be analyzed for various parameters, including protein levels, glucose levels, and the presence of white blood cells or other abnormal substances.
The treatment of elevated CSF protein levels depends on the underlying cause of the condition. For example, if the cause is an infection, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed. In the case of an autoimmune disorder, such as multiple sclerosis, treatment may involve immunomodulatory therapies or other disease-modifying medications.
In some cases, elevated CSF protein levels may be a feature of a more serious underlying condition, such as a brain or spinal cord tumor. In these situations, prompt medical attention is essential to ensure timely diagnosis and treatment.
Prevention and Prognosis
While it is not possible to prevent all cases of elevated CSF protein levels, there are certain measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing some of the underlying conditions. For example, practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated against infectious diseases, and avoiding head or spinal cord injuries can all help to minimize the risk of developing conditions that can lead to elevated CSF protein levels.
The prognosis for individuals with elevated CSF protein levels depends on the underlying cause of the condition. In some cases, such as meningitis or encephalitis, prompt treatment can lead to a full recovery. However, in other cases, such as multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injury, the prognosis may be more uncertain, and ongoing medical management may be necessary to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
What are the common causes of elevated CSF protein levels?
+Elevated CSF protein levels can be caused by various conditions, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and injuries that affect the central nervous system. Some of the most common causes include meningitis, encephalitis, Guillain-Barré Syndrome, multiple sclerosis, and spinal cord injury.
How are elevated CSF protein levels diagnosed?
+To diagnose the cause of elevated CSF protein levels, a healthcare professional will typically perform a lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, to collect a sample of the spinal fluid. The CSF sample will then be analyzed for various parameters, including protein levels, glucose levels, and the presence of white blood cells or other abnormal substances.
What is the treatment for elevated CSF protein levels?
+The treatment of elevated CSF protein levels depends on the underlying cause of the condition. For example, if the cause is an infection, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed. In the case of an autoimmune disorder, such as multiple sclerosis, treatment may involve immunomodulatory therapies or other disease-modifying medications.