Sloughy Wounds Management: Healing Guide
The management of sloughy wounds is a complex and challenging process that requires a deep understanding of wound healing principles, careful assessment, and a multifaceted approach to treatment. Sloughy wounds, characterized by the presence of slough, a soft, moist, and necrotic tissue, pose significant barriers to healing, including increased risk of infection, prolonged healing times, and potential for further tissue damage. Effective management of these wounds demands a holistic approach that addresses not only the wound itself but also the underlying factors contributing to its development and persistence.
Understanding Sloughy Wounds
At the core of managing sloughy wounds is a thorough understanding of their pathophysiology. The presence of slough indicates a wound that is stuck in the inflammatory phase of healing, where the body’s natural response to injury has become dysregulated. This phase is marked by the accumulation of dead cells, bacteria, and debris, which must be removed for healing to progress. Key factors contributing to the development of sloughy wounds include inadequate wound care, poor circulation, diabetes, and nutritional deficiencies. Recognizing these factors is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Assessment of Sloughy Wounds
A comprehensive assessment of the wound is the first step in its management. This assessment should include:
- Visual Inspection: Evaluate the wound for signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, swelling, and purulent discharge. Note the color, consistency, and adherence of the slough.
- Wound Measurement: Accurately measure the wound’s length, width, and depth to monitor progress and guide treatment decisions.
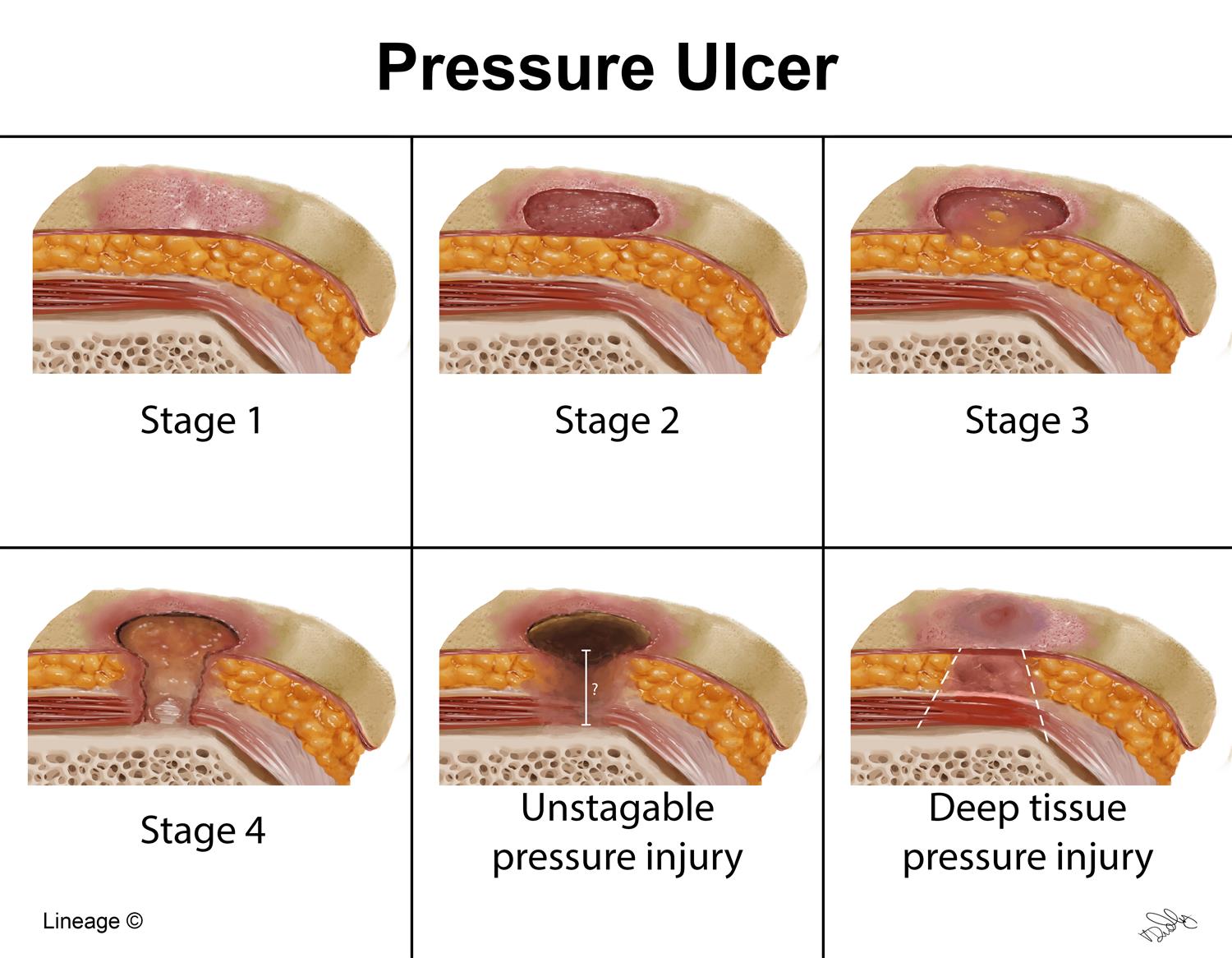
- Tissue Assessment: Use tools like the Bates-Jensen Wound Assessment Tool to evaluate the extent of tissue damage and the presence of slough, eschar, or granulation tissue.
- Patient History: Consider the patient’s medical history, including diabetes, vascular diseases, and previous wound healing issues, as these can significantly impact wound healing.
Treatment Strategies for Sloughy Wounds
The treatment of sloughy wounds involves debridement, wound dressing, and management of underlying conditions.
Debridement
Debridement, the removal of dead tissue, is critical in managing sloughy wounds. Methods include:
- Autolytic Debridement: Using dressings that create a moist environment, allowing the body to break down dead tissue naturally.
- Mechanical Debridement: Physically removing dead tissue through methods like wound irrigation or the use of wet-to-dry dressings.
- Surgical Debridement: Surgical removal of dead tissue, typically reserved for extensive necrosis or when other methods are ineffective.
Wound Dressing
The choice of dressing depends on the wound’s stage, amount of exudate, and presence of infection. Hydrogels, foams, and alginate dressings are commonly used for sloughy wounds due to their ability to manage exudate and promote a moist healing environment.
Management of Underlying Conditions
Addressing the underlying causes of sloughy wounds, such as diabetes, poor circulation, and nutritional deficiencies, is vital for promoting healing. This may involve working with other healthcare professionals to optimize the patient’s overall health.
Role of Nutrition in Wound Healing
Nutrition plays a critical role in wound healing, particularly for sloughy wounds. Adequate intake of proteins, vitamins (especially Vitamin C and A), and minerals (like zinc) is essential for tissue repair and regeneration. Malnutrition can significantly impede the healing process, making nutritional assessment and support an integral part of wound management.
Preventing Infection in Sloughy Wounds
Preventing infection is crucial in the management of sloughy wounds. Strategies include:
- Proper Wound Cleansing: Regular cleansing with saline solution to remove bacteria and debris.
- Antimicrobial Dressings: Using dressings with antimicrobial properties to reduce bacterial load.
- Monitoring for Signs of Infection: Regular assessment for signs of infection, with prompt intervention if suspected.
Patient Education and Support
Educating patients and their caregivers about wound management, including dressing changes, signs of infection, and the importance of follow-up appointments, is vital for successful healing. Support systems, such as wound care clinics and home healthcare services, can provide the ongoing care and monitoring needed for optimal outcomes.
Future Directions in Sloughy Wounds Management
Advancements in technology and biomedical research are continually evolving the landscape of wound care. Emerging treatments, such as the use of bioengineered skin substitutes, growth factor therapy, and negative pressure wound therapy, offer promising solutions for patients with sloughy wounds. However, these innovations must be integrated into practice thoughtfully, considering both their potential benefits and limitations.
Conclusion
The management of sloughy wounds is a nuanced and multifaceted challenge that requires a deep understanding of wound healing, careful assessment, and a patient-centered approach to care. By addressing the wound itself, as well as the underlying factors contributing to its development, healthcare providers can promote effective healing, improve patient outcomes, and enhance quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best way to clean a sloughy wound?
+Cleaning a sloughy wound should be done gently with saline solution to remove debris and bacteria without damaging the surrounding tissue. Avoid using harsh soap or hydrogen peroxide, as these can impede healing.
How often should I change the dressing on a sloughy wound?
+The frequency of dressing changes depends on the type of dressing and the amount of exudate. Generally, dressings should be changed when they become saturated or as recommended by the healthcare provider, typically every 1-3 days.
Can sloughy wounds be prevented?
+While not all sloughy wounds can be prevented, risk factors such as diabetes, poor circulation, and nutritional deficiencies can be managed through lifestyle changes and medical intervention. Early detection and proper care of wounds can also prevent the development of slough.
Advanced Techniques in Wound Healing
The field of wound healing is rapidly advancing, with new technologies and treatments being developed to address the complex challenges of sloughy wounds. From the use of stem cells to bioactive dressings, these innovations offer hope for improved healing outcomes and reduced morbidity for patients with chronic wounds. As research continues to uncover the intricacies of wound healing, integrating these findings into clinical practice will be crucial for providing the best possible care for individuals with sloughy wounds.
