Olfactory Bulb In Sheep Brain
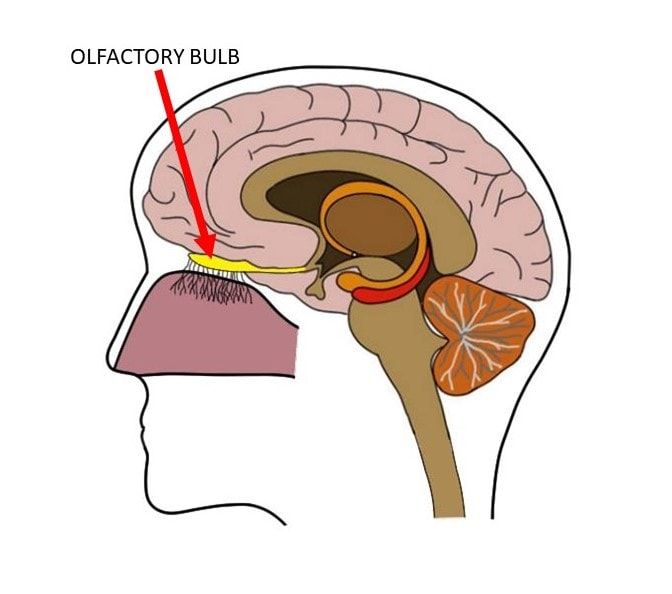
The olfactory bulb, a critical component of the olfactory system, plays a pivotal role in the perception and processing of smells in various species, including sheep. Located in the forebrain, the olfactory bulb is responsible for receiving and interpreting sensory information from the olfactory receptors in the nose. In sheep, the structure and function of the olfactory bulb are closely linked to their unique behaviors and survival strategies, highlighting the significance of olfaction in their daily lives.
Structure of the Olfactory Bulb in Sheep
The olfactory bulb in sheep, similar to other mammals, is divided into distinct layers, each with specific functions. These layers include the olfactory nerve layer, the glomerular layer, the external plexiform layer, the mitral cell layer, and the granule cell layer. The glomerular layer, where the axons of olfactory receptor neurons synapse with the dendrites of mitral and tufted cells, is particularly notable for its role in the initial processing of olfactory information. The specific organization and the density of glomeruli in sheep can influence their ability to detect and discriminate between different odors.
Function of the Olfactory Bulb in Sheep
The primary function of the olfactory bulb in sheep is to process the chemical signals detected by the olfactory receptors. These chemical signals, or odorants, bind to specific receptors on the surface of olfactory receptor neurons, triggering a signal that is transmitted to the olfactory bulb. Within the olfactory bulb, the information is further processed and refined, allowing the sheep to perceive and differentiate between a wide range of smells. This ability is crucial for sheep as they rely heavily on their sense of smell for finding food, recognizing predators, and communicating with other sheep.
Role in Behavior and Survival
The olfactory bulb’s role in sheep behavior and survival cannot be overstated. For instance, a sheep’s ability to detect the scent of its lamb is essential for maternal bonding and care. Similarly, the detection of predator scents can trigger a flight response, protecting the sheep from potential danger. The sense of smell also plays a crucial role in foraging behavior, enabling sheep to select nutritious food sources and avoid toxic plants. Furthermore, olfactory cues are involved in social recognition among sheep, facilitating the establishment and maintenance of social hierarchies within flocks.
Comparison with Other Species
When comparing the olfactory bulb in sheep to that in other species, such as humans or rodents, several differences and similarities emerge. For example, the olfactory bulb in rodents is significantly larger relative to their brain size compared to humans, reflecting the greater importance of olfaction in their behavioral and survival strategies. Sheep, falling somewhere in between, demonstrate a well-developed olfactory system that is tailored to their specific environmental and social needs. Understanding these comparisons can provide insights into the evolutionary pressures that have shaped the development of the olfactory system in different species.
Impact of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as exposure to pollutants or changes in dietary habits, can impact the development and function of the olfactory bulb in sheep. For instance, prenatal exposure to certain pollutants has been shown to affect the development of the olfactory system in various species, potentially leading to impairments in olfactory function. Similarly, dietary changes can influence the composition of olfactory receptors and the processing of olfactory information, highlighting the complex interplay between environmental factors, olfactory perception, and behavior.
Future Research Directions
Future research directions in the study of the olfactory bulb in sheep could include investigations into the molecular mechanisms underlying olfactory perception and processing, as well as the impact of environmental and genetic factors on olfactory function. The development of new methodologies, such as advanced imaging techniques or genetic editing tools, could provide unprecedented insights into the structure and function of the olfactory bulb, contributing to our understanding of the complex relationships between olfaction, behavior, and survival in sheep.
Practical Applications
The study of the olfactory bulb in sheep has several practical applications, ranging from improvements in animal welfare and productivity to the development of novel strategies for controlling parasite burdens or enhancing foraging behaviors. For example, understanding the specific odors that attract or repel sheep could inform the development of more effective grazing management systems or the creation of odor-based deterrents for predators. Additionally, insights into the neural basis of olfactory perception could contribute to the design of enriched environments that stimulate the olfactory system, thereby enhancing the cognitive and emotional well-being of sheep.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the olfactory bulb plays a critical role in the life of sheep, influencing their behavior, social interactions, and survival strategies. Through its intricate structure and complex function, the olfactory bulb enables sheep to navigate their environment, recognize significant stimuli, and make decisions that are crucial for their well-being. As research continues to unveil the mysteries of the olfactory system, it is clear that the study of the olfactory bulb in sheep will remain an essential area of investigation, offering insights not only into the biology of these animals but also into the broader principles of olfactory perception and its role in the lives of species across the animal kingdom.
What is the primary function of the olfactory bulb in sheep?
+The primary function of the olfactory bulb in sheep is to process the chemical signals detected by the olfactory receptors, enabling the perception and differentiation of various smells. This ability is crucial for behaviors such as finding food, recognizing predators, and communicating with other sheep.
How does the olfactory bulb contribute to the social behavior of sheep?
+The olfactory bulb plays a significant role in the social behavior of sheep by facilitating the recognition of individual members of the flock, maternal bonding, and the establishment of social hierarchies. Olfactory cues are essential for these social interactions, which are vital for the cohesive functioning of sheep societies.
Can environmental factors impact the development and function of the olfactory bulb in sheep?
+Yes, environmental factors such as exposure to pollutants, changes in dietary habits, and other external influences can impact the development and function of the olfactory bulb in sheep. These factors can affect the composition of olfactory receptors, the processing of olfactory information, and ultimately, the behavior and well-being of the animals.