Muscles And Tendons Of Foot
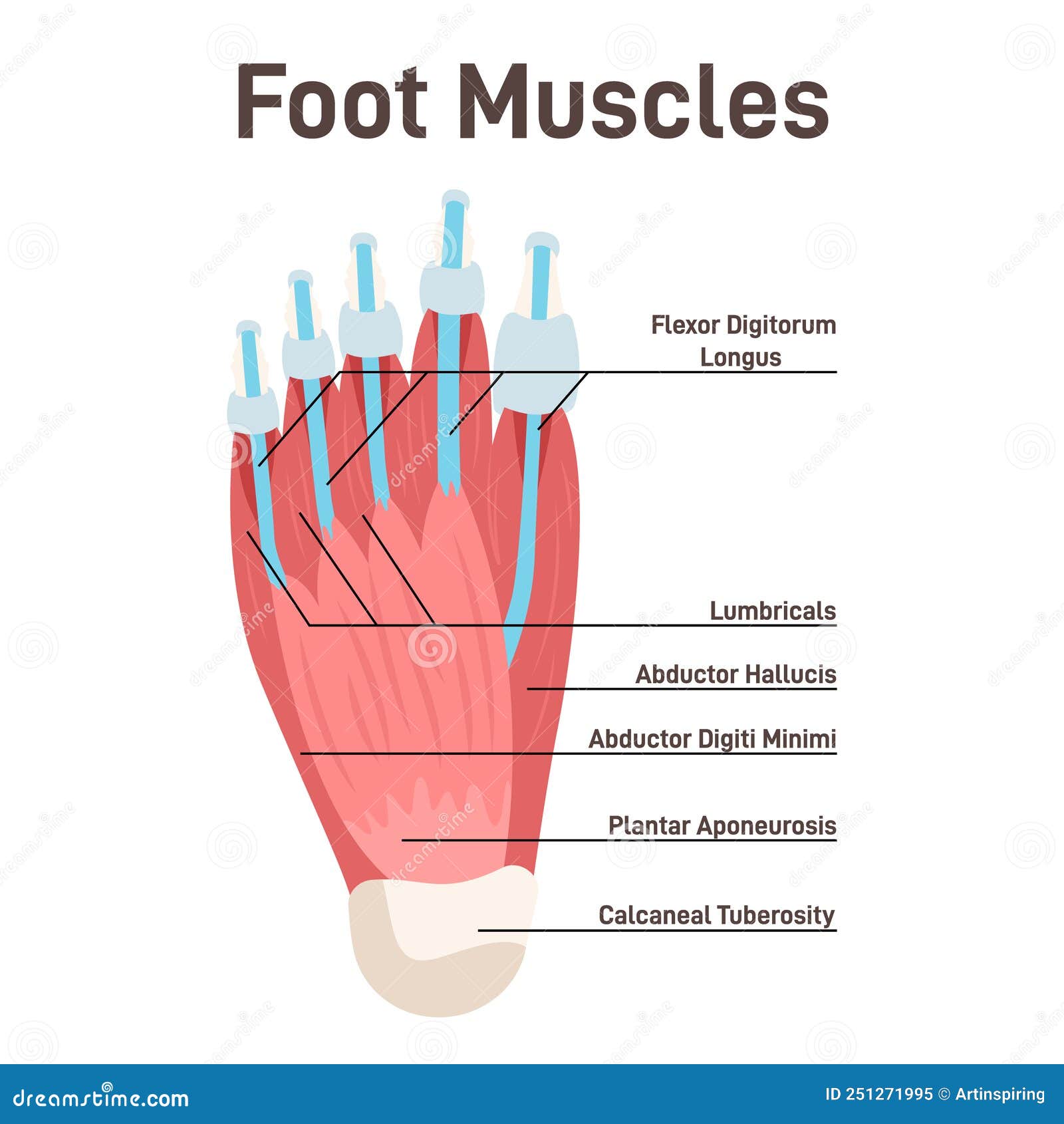
The human foot is a complex and fascinating structure, comprising 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Among these, the muscles and tendons play a crucial role in facilitating movement, maintaining balance, and supporting the body’s weight. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy and function of the muscles and tendons of the foot, exploring their significance in our daily lives.
Anatomy of Foot Muscles
The muscles of the foot can be broadly categorized into two groups: intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic muscles are those that originate and insert within the foot itself, whereas extrinsic muscles originate from the lower leg and insert into the foot.
- Intrinsic Muscles: There are 20 intrinsic muscles in the foot, which can be further divided into four layers. These muscles are responsible for toe movements, such as flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction. The intrinsic muscles include:
- Abductor hallucis
- Flexor hallucis brevis
- Adductor hallucis
- Quadratus plantae
- Lumbricals
- Interossei
- Extrinsic Muscles: The extrinsic muscles of the foot include:
- Gastrocnemius
- Soleus
- Peroneus longus
- Peroneus brevis
- Tibialis anterior
- Tibialis posterior
These muscles play a vital role in ankle movement, foot stability, and balance.
Tendons of the Foot
Tendons are strong, fibrous cords that connect muscles to bones. In the foot, tendons facilitate movement by transmitting the forces generated by muscle contraction to the bones. The tendons of the foot include: 1. Achilles Tendon: The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the foot, connecting the calf muscles (gastrocnemius and soleus) to the calcaneus bone. It plays a crucial role in plantarflexion, the movement that allows us to push off the ground and walk. 2. Peroneal Tendons: The peroneal tendons connect the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis muscles to the bones in the foot. They help stabilize the foot and ankle during movements like eversion and inversion. 3. Flexor Tendons: The flexor tendons connect the flexor muscles (flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor digitorum brevis) to the bones in the toes. They facilitate toe flexion and extension.
Functions of Muscles and Tendons
The muscles and tendons of the foot work in tandem to perform a variety of functions essential for daily activities. These include:
- Movement: The muscles and tendons of the foot enable movements like walking, running, jumping, and balance.
- Stability: The intrinsic and extrinsic muscles, along with the tendons, help maintain foot stability and prevent excessive pronation or supination.
- Support: The muscles and tendons of the foot support the body’s weight and facilitate weight transfer during movements.
- Balance: The muscles and tendons of the foot play a crucial role in maintaining balance and preventing falls.
Injuries and Disorders
The muscles and tendons of the foot are susceptible to various injuries and disorders, including: 1. Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons, often caused by overuse or repetitive strain. 2. Strains: Muscle strains, which can occur due to sudden contractions or overstretching. 3. Tears: Tendon tears, which can be partial or complete, and may require surgical intervention. 4. Foot drop: A condition characterized by weakness or paralysis of the muscles responsible for foot movement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the muscles and tendons of the foot are complex structures that work together to facilitate movement, maintain balance, and support the body’s weight. Understanding the anatomy and function of these structures is essential for appreciating the intricate mechanisms that govern our daily lives. By recognizing the importance of foot health and taking preventive measures, we can reduce the risk of injuries and disorders, ensuring optimal foot function and overall well-being.
What is the function of the Achilles tendon in the foot?
+The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles to the calcaneus bone and plays a crucial role in plantarflexion, facilitating movements like walking and running.
What are the intrinsic muscles of the foot responsible for?
+The intrinsic muscles of the foot are responsible for toe movements, such as flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
What is foot drop, and how is it related to the muscles and tendons of the foot?
+Foot drop is a condition characterized by weakness or paralysis of the muscles responsible for foot movement, often caused by nerve damage or muscle weakness.
