Metatarsal Fracture: Recover In 3 Months Or Less
The human foot is a complex structure consisting of 26 bones, with the metatarsals being five long bones located in the midfoot region. These bones play a crucial role in weight-bearing, balance, and mobility. A metatarsal fracture, which is a break in one of these bones, can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. The recovery period for such an injury can vary depending on the severity and location of the fracture, as well as the effectiveness of the treatment approach. However, with proper care and rehabilitation, it is possible to recover from a metatarsal fracture in three months or less.
Understanding the types of metatarsal fractures is essential for devising an appropriate treatment plan. Fractures can be classified into two main categories: stress fractures and acute fractures. Stress fractures are small cracks in the bone, often caused by repetitive stress or overuse, and are common among athletes. Acute fractures, on the other hand, are characterized by a sudden and severe break in the bone, typically resulting from a traumatic event. The location of the fracture also plays a significant role in determining the recovery time, with fractures closer to the toe (distal metatarsal fractures) generally having a faster recovery than those closer to the ankle (proximal metatarsal fractures).
Treatment Approaches for Metatarsal Fractures
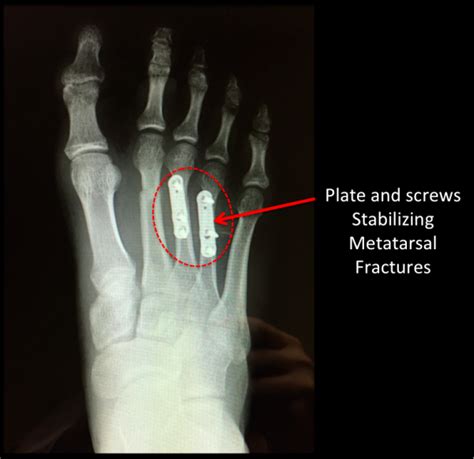
The primary goal of treating a metatarsal fracture is to ensure proper healing, minimize discomfort, and restore full mobility and function to the foot. Treatment options can range from conservative management to surgical intervention, depending on the fracture’s severity and stability. Conservative treatment typically involves immobilization, either through casting or the use of a protective boot, to allow the bone to heal naturally. This method is often effective for stress fractures and non-displaced acute fractures. For more severe or displaced fractures, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign and stabilize the bone, facilitating proper healing and minimizing the risk of complications.
Immobilization is a critical component of conservative treatment for metatarsal fractures. By restricting movement and reducing stress on the affected bone, immobilization creates an environment conducive to natural healing. The duration of immobilization varies but typically ranges from 4 to 8 weeks, during which time the patient may be required to use crutches to avoid putting weight on the affected foot. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the recovery process, helping to regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the foot and ankle. A well-structured rehabilitation program can significantly reduce the overall recovery time and improve outcomes.
Rehabilitation Strategies for Enhanced Recovery
Effective rehabilitation following a metatarsal fracture involves a gradual and progressive approach, tailored to the individual’s healing process and specific needs. The initial phases focus on pain management, swelling reduction, and maintaining range of motion through gentle exercises. As the fracture heals, the intensity of the physical therapy program increases, incorporating strengthening exercises, balance training, and functional activities to mimic daily movements and sports-specific actions for athletes. The incorporation of orthotic devices, such as shoe inserts or braces, can also be beneficial in providing additional support and stability to the foot during the recovery period.
Nutritional factors and overall health also contribute significantly to the healing process. A diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and other nutrients essential for bone health can support the fracture repair process. Furthermore, managing any underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, which can impair healing, is crucial for a successful recovery. Smoking cessation is also highly recommended, as smoking can negatively impact bone healing and prolong recovery times.
Technological Advancements in Fracture Recovery
Recent advancements in medical technology have introduced innovative treatments and tools aimed at enhancing the recovery process for metatarsal fractures. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, which involves injecting platelet-rich plasma into the fracture site to stimulate healing, has shown promise in accelerating recovery times. Additionally, the use of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) has been explored as a non-invasive method to enhance fracture healing by stimulating cellular activity and increasing blood flow to the affected area. While these technologies are not universally available and their effectiveness can vary, they represent the evolving nature of fracture treatment and the ongoing quest for improved outcomes.
Navigating the Road to Recovery
Recovering from a metatarsal fracture in three months or less requires a combination of effective treatment, diligent adherence to rehabilitation protocols, and a supportive environment. Patients must be proactive in their recovery, following post-treatment instructions carefully, attending physical therapy sessions regularly, and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers about their progress and any concerns. The psychological aspect of recovery should not be underestimated, as the frustration of limited mobility and the pressure to return to normal activities can be significant. Thus, seeking support from family, friends, or professional counselors can be invaluable in navigating the emotional challenges that often accompany physical rehabilitation.
In conclusion, while metatarsal fractures can present significant challenges, the integration of advanced treatment strategies, personalized rehabilitation programs, and a holistic approach to healing can facilitate recovery in three months or less. As medical science continues to evolve, the development of new technologies and treatment methodologies holds promise for even more effective and efficient management of these injuries, ultimately aiming to restore individuals to their full potentials with minimal downtime.
What are the most common causes of metatarsal fractures?
+Metatarsal fractures can result from a variety of causes, including direct blows or trauma to the foot, overuse or repetitive stress from activities like running or dancing, and osteoporosis, which weakens bones and makes them more susceptible to fractures.
How can I prevent metatarsal fractures?
+Prevention of metatarsal fractures involves a combination of strategies, including wearing appropriate footwear for activities, gradually increasing exercise intensity to avoid overuse, maintaining a healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin D to support bone health, and avoiding smoking.
What are the signs that a metatarsal fracture is healing properly?
+Proper healing of a metatarsal fracture can be indicated by a decrease in pain, particularly at the fracture site, an increase in the ability to bear weight on the foot without discomfort, improvement in range of motion and strength in the foot and ankle, and evidence of bone union on follow-up X-rays.


