Ir Functional Groups
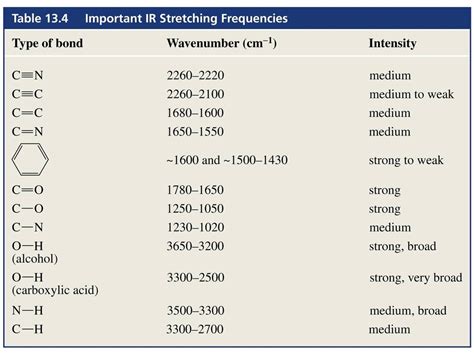
In the realm of organic chemistry, functional groups are the essential components that dictate the properties and reactivity of molecules. These groups of atoms, typically consisting of a central atom bonded to other atoms or groups of atoms, are responsible for the characteristic chemical behavior of a molecule. The study of functional groups is crucial in understanding the diverse range of reactions and transformations that occur in organic chemistry.
To grasp the significance of functional groups, it’s essential to explore the various types that exist and their distinct properties. One of the primary classifications of functional groups is based on their electronegativity, which influences their polarity and reactivity. For instance, hydroxyl (-OH), amino (-NH2), and carboxyl (-COOH) groups are polar and tend to form hydrogen bonds, whereas alkyl (-R) and aryl (-Ar) groups are nonpolar and relatively inert.
1. Hydroxyl (-OH) Group
The hydroxyl group, a fundamental component of alcohols, is a prime example of a polar functional group. This group is characterized by its ability to form hydrogen bonds, which are crucial in determining the physical and chemical properties of alcohols. The hydroxyl group’s electronegativity also makes it susceptible to nucleophilic substitution reactions, where the hydroxyl group acts as a leaving group.
Properties of Hydroxyl Group:
- Polarity: The hydroxyl group is polar due to the significant difference in electronegativity between oxygen and hydrogen.
- Reactivity: It is relatively reactive, participating in reactions such as esterification and etherification.
- Solubility: Compounds with hydroxyl groups tend to be soluble in water due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds.
2. Amino (-NH2) Group
Amino groups, found in amines, are another crucial class of functional groups. These groups are basic in nature and can accept protons, making them essential in various biological and chemical processes. The amino group’s ability to participate in hydrogen bonding and its basicity contribute to the unique properties of amines.
Properties of Amino Group:
- Basicity: Amino groups are basic and can react with acids to form salts.
- Reactivity: They are reactive towards alkylating agents and can undergo nucleophilic substitution.
- Solubility: Compounds with amino groups often exhibit increased solubility in water due to their ability to engage in hydrogen bonding.
3. Carboxyl (-COOH) Group
The carboxyl group, characteristic of carboxylic acids, is both acidic and polar. This dual nature allows carboxylic acids to participate in a wide range of reactions, including acid-base reactions and condensation reactions. The carboxyl group’s acidity is due to its ability to donate a proton (H+), making it a key functional group in organic synthesis.
Properties of Carboxyl Group:
- Acidity: Carboxyl groups are acidic, capable of donating a proton.
- Reactivity: They are reactive towards bases and can undergo esterification and amidation reactions.
- Solubility: Carboxylic acids typically exhibit good solubility in water due to their polarity and ability to form hydrogen bonds.
Functional Groups in Reactions
The presence and type of functional groups on a molecule can greatly influence its reactivity and the types of reactions it can undergo. For example, the hydroxyl group in alcohols can be replaced by other groups through nucleophilic substitution, while the carboxyl group in carboxylic acids can react with amines to form amides. Understanding these reactions is essential for synthesizing new compounds and modifying existing ones.
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
Nucleophilic substitution reactions involve the replacement of a leaving group (such as a hydroxyl or halide group) with a nucleophile. These reactions are fundamental in organic chemistry and are often used to introduce new functional groups into a molecule.
Condensation Reactions
Condensation reactions, such as esterification and amidation, involve the combination of two molecules with the loss of a small molecule, typically water. These reactions are crucial for forming new bonds between molecules and are used extensively in organic synthesis.
Conclusion
Functional groups are the cornerstone of organic chemistry, determining the chemical behavior and properties of molecules. Understanding the diverse range of functional groups, their properties, and their roles in reactions is essential for chemists and researchers aiming to synthesize new compounds, modify existing ones, and develop new materials and drugs. The unique characteristics of each functional group, such as polarity, reactivity, and ability to participate in hydrogen bonding, influence the physical and chemical properties of molecules, making them vital components in the vast array of organic compounds found in nature and synthesized in laboratories.
FAQ Section
What are the primary characteristics that distinguish different functional groups?
+The primary characteristics include electronegativity, polarity, and the ability to form hydrogen bonds, which influence their reactivity and the physical and chemical properties of the molecules they are part of.
How do functional groups influence the solubility of organic compounds?
+Functional groups that can form hydrogen bonds, such as hydroxyl and amino groups, tend to increase the solubility of organic compounds in water. Nonpolar groups, on the other hand, decrease water solubility.
What role do functional groups play in the reactivity of organic molecules?
+Functional groups are the primary sites of reaction in organic molecules. They dictate the types of reactions a molecule can undergo and the conditions under which these reactions occur, due to their unique electronic and steric properties.
Can functional groups be modified or exchanged in a molecule?
+Yes, functional groups can be modified or exchanged through various organic reactions. This ability is fundamental in organic synthesis, where chemists aim to introduce or modify functional groups to achieve specific chemical or physical properties.
How do the properties of functional groups contribute to the biological activity of molecules?
+The properties of functional groups, such as their ability to form hydrogen bonds or act as electron donors/acceptors, play a crucial role in the interaction between molecules and biological targets, such as enzymes or receptors. These interactions are key to the biological activity of drugs and other bioactive compounds.

