Income Tax Az
Navigating the complexities of income tax can be a daunting task, especially when considering the unique regulations and laws that apply to specific regions. In the state of Arizona, understanding the income tax landscape is crucial for both individuals and businesses to ensure compliance and optimize their financial obligations. The Arizona income tax system, like many others, is designed to fund public services and infrastructure, but its specifics can vary significantly from federal income tax laws and those of other states.
Understanding Arizona Income Tax Basics
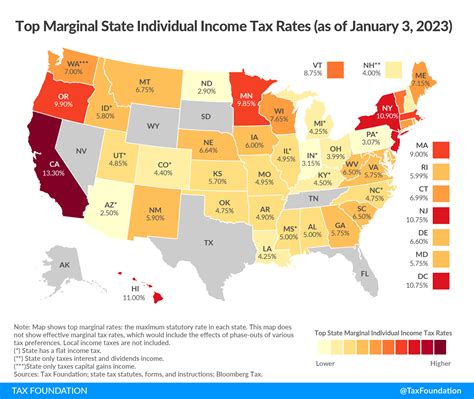
Arizona is one of the states with a progressive income tax system, meaning that higher income earners are subject to higher tax rates. The state’s income tax rates range from 2.59% to 4.54%, depending on the taxpayer’s filing status and income level. This progressive system aims to distribute the tax burden more evenly, with higher-income individuals contributing a larger percentage of their income towards state revenues.
Tax Brackets and Rates
As of the last update, Arizona has four income tax brackets:
- 2.59%: This is the lowest tax rate, applied to the first 27,825 of taxable income for single filers and 55,650 for joint filers.
- 3.34%: Applies to income between 27,826 and 89,450 for single filers, and 55,651 to 178,900 for joint filers.
- 4.17%: This rate is applied to income between 89,451 and 182,100 for single filers, and 178,901 to 364,200 for joint filers.
- 4.54%: The highest tax rate, applied to income above 182,100 for single filers and 364,200 for joint filers.
These rates and brackets are subject to change, and it’s essential to consult the Arizona Department of Revenue or a tax professional for the most current information.
Tax Credits and Deductions
Arizona offers various tax credits and deductions to help reduce the income tax liability. These can include credits for contributions to public schools, credits for qualified charitable organizations, and deductions for mortgage interest and property taxes, among others. The Arizona Charitable Tax Credit, for example, allows taxpayers to claim a credit for donations made to qualified charitable organizations, up to certain limits.
Filing Requirements
The deadline for filing Arizona state income tax returns typically aligns with the federal tax filing deadline, which is usually April 15th of each year. Taxpayers can file their Arizona income tax returns electronically or by mail, and those who are due a refund can expect to receive it more quickly by choosing direct deposit.
Tax Planning Strategies
Given the progressive nature of Arizona’s income tax system, tax planning can play a significant role in minimizing tax liabilities. Strategies might include maximizing deductions and credits, considering timing for income recognition and expense deductions, and utilizing tax-advantaged retirement savings vehicles. Consulting with a tax professional can help individuals and businesses tailor a tax strategy to their specific situation.
Impact of Federal Tax Changes
Federal tax law changes, such as those enacted through the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), can have implications for state income taxes, including Arizona’s. For instance, the TCJA’s limitation on the state and local tax (SALT) deduction can affect how much taxpayers can deduct from their federal taxable income, potentially influencing their state tax liability as well.
Conclusion
Arizona’s income tax system, while similar in many respects to other states, has its unique characteristics and considerations. Understanding these specifics, from tax rates and brackets to credits and deductions, is vital for taxpayers in the state. As with any tax system, changes can occur, making it essential to stay informed about updates and adjustments that might affect individual or business tax obligations.
FAQ Section
What are the income tax rates in Arizona?
+Arizona has a progressive income tax system with rates ranging from 2.59% to 4.54%, depending on the taxpayer’s filing status and income level.
What tax credits are available in Arizona?
+Arizona offers several tax credits, including credits for contributions to public schools and qualified charitable organizations, which can help reduce tax liability.
How do I file my Arizona state income tax return?
+Arizona state income tax returns can be filed electronically or by mail. The deadline typically aligns with the federal tax filing deadline, which is April 15th of each year.
Are there any specific tax planning strategies for Arizona taxpayers?
+Yes, strategies such as maximizing deductions and credits, timing income recognition and expense deductions, and utilizing tax-advantaged retirement savings can help minimize tax liabilities in Arizona.
How do federal tax law changes affect Arizona state income tax?
+Federal tax law changes, such as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, can have implications for Arizona state income tax, including limitations on deductions that can affect state tax liability.


