Hydrogen Cyanide Structure
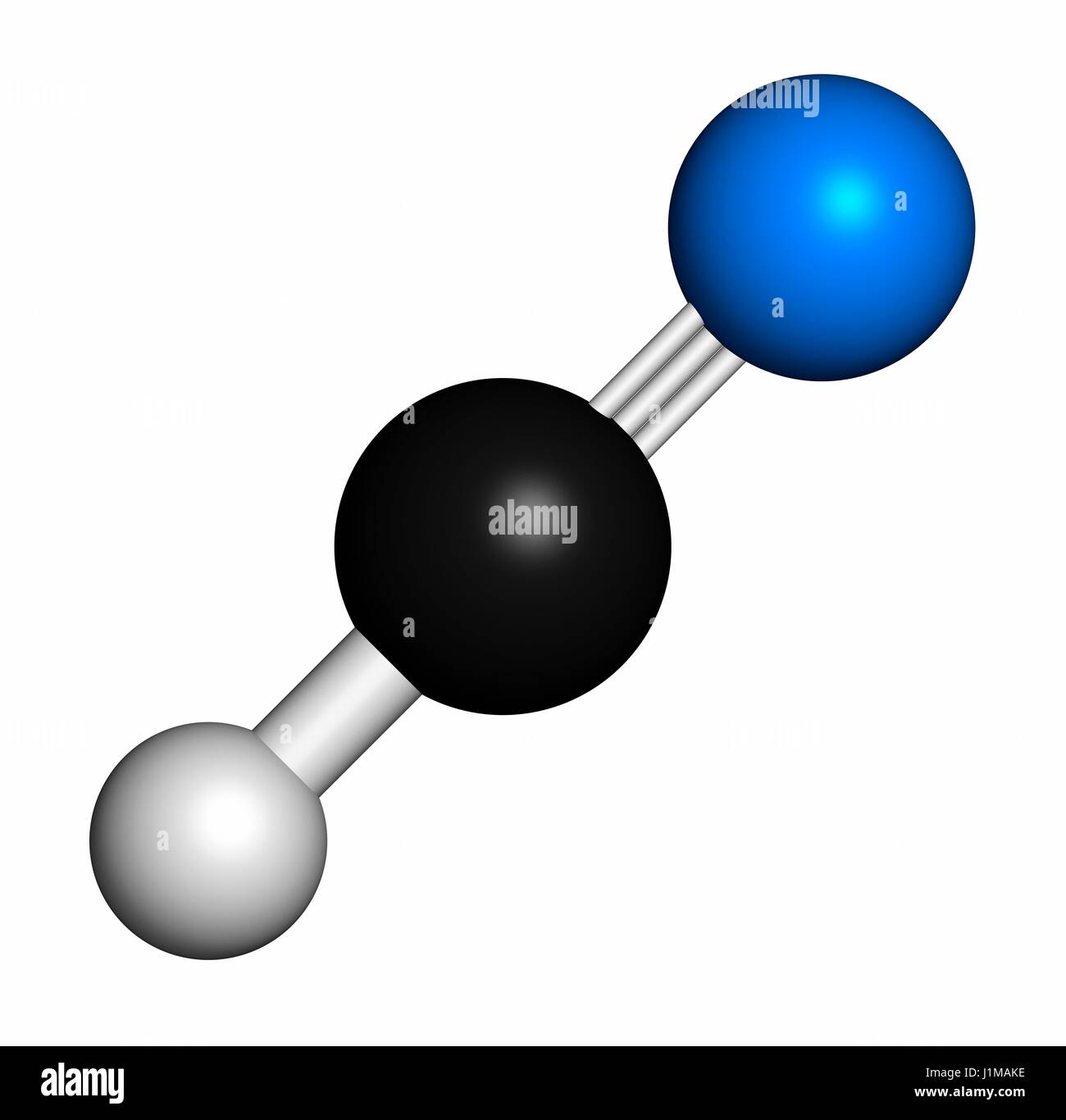
Hydrogen cyanide, also known as hydrocyanic acid or prussic acid, is a chemical compound with the molecular formula HCN. It is a colorless, highly toxic, and volatile liquid that boils at 25.6°C. The structure of hydrogen cyanide is a crucial aspect of its properties and reactivity, making it an essential component in various chemical reactions and industrial applications.
At the molecular level, hydrogen cyanide consists of a hydrogen atom bonded to a cyanide group, which comprises a carbon atom triple-bonded to a nitrogen atom. This arrangement results in a linear molecular geometry, with the hydrogen atom at one end and the cyanide group at the other. The carbon-nitrogen triple bond is a key feature of the cyanide group, contributing to its exceptional stability and reactivity.
The bond lengths in hydrogen cyanide are also noteworthy. The carbon-nitrogen bond length is approximately 1.16 Å, which is shorter than a typical carbon-nitrogen single bond. This shortened bond length is a consequence of the triple bond between the carbon and nitrogen atoms, which results in a stronger and more stable bond. The hydrogen-carbon bond length is about 1.06 Å, which is slightly shorter than a standard hydrogen-carbon single bond.
The electronegativity of the atoms in hydrogen cyanide plays a significant role in determining its molecular properties. The nitrogen atom, with an electronegativity of 3.04, is the most electronegative atom in the molecule, followed by the carbon atom with an electronegativity of 2.55. The hydrogen atom has an electronegativity of 2.20. This difference in electronegativity leads to a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge on the nitrogen atom, resulting in a net dipole moment of 2.98 D.
The structure of hydrogen cyanide has significant implications for its chemical properties and reactivity. The cyanide group is a strong nucleophile, making hydrogen cyanide an effective reactant in various organic synthesis reactions. The compound is also highly toxic, as it can bind to the iron atom in cytochrome c oxidase, an enzyme essential for cellular respiration, thereby inhibiting cellular energy production.
In terms of industrial applications, hydrogen cyanide is used as an intermediate in the production of various chemicals, such as adiponitrile, which is used in the manufacture of nylon. It is also employed in the mining industry for the extraction of gold and silver through the cyanidation process.
To further understand the structure and properties of hydrogen cyanide, it is essential to examine its vibrational modes and spectroscopic characteristics. The compound exhibits several distinct vibrational modes, including a strong C-N stretching band at approximately 2090 cm^-1 and a weaker H-C stretching band at around 3300 cm^-1. These vibrational modes are sensitive to the molecular environment and can be used to monitor changes in the compound’s structure and reactivity.
The structure of hydrogen cyanide is a critical factor in its reactivity and toxicity. Understanding the molecular geometry, bond lengths, and electronegativity of the atoms in the compound can provide valuable insights into its chemical properties and potential applications.
The chemical properties of hydrogen cyanide are also influenced by its thermodynamic characteristics. The compound has a standard enthalpy of formation of -135.1 kJ/mol and a standard entropy of 112.9 J/mol·K. These thermodynamic parameters are essential in predicting the spontaneity and feasibility of chemical reactions involving hydrogen cyanide.
In conclusion, the structure of hydrogen cyanide plays a vital role in determining its chemical properties, reactivity, and industrial applications. The compound’s linear molecular geometry, triple-bonded cyanide group, and distinct electronegativity values contribute to its unique characteristics and make it an essential component in various chemical reactions and industrial processes.
Key Steps to Understanding Hydrogen Cyanide Structure
- Recognize the molecular formula of hydrogen cyanide as HCN.
- Identify the linear molecular geometry and triple-bonded cyanide group.
- Understand the bond lengths and electronegativity values of the atoms in the compound.
- Analyze the implications of the structure on the chemical properties and reactivity of hydrogen cyanide.
- Explore the industrial applications and potential risks associated with the compound.
By examining the structure and properties of hydrogen cyanide, researchers and scientists can gain a deeper understanding of this complex and highly reactive compound, ultimately leading to the development of new applications and safety protocols.
What is the molecular formula of hydrogen cyanide?
+The molecular formula of hydrogen cyanide is HCN.
What is the shape of the hydrogen cyanide molecule?
+The hydrogen cyanide molecule has a linear shape.
What is the bond length between the carbon and nitrogen atoms in hydrogen cyanide?
+The bond length between the carbon and nitrogen atoms in hydrogen cyanide is approximately 1.16 Å.
What are some industrial applications of hydrogen cyanide?
+Hydrogen cyanide is used as an intermediate in the production of various chemicals, such as adiponitrile, and in the mining industry for the extraction of gold and silver through the cyanidation process.
