How Much Do Reserves Get Paid 2024? Benefits Inside
The life of a reserve in the military is one of readiness and flexibility. Reserves play a crucial role in the military’s ability to respond to a wide range of situations, from natural disasters to combat operations. But how much do reserves get paid, and what benefits do they receive? In this article, we’ll delve into the world of reserve pay and benefits, exploring the intricacies of the compensation system and the advantages of serving in the reserves.
Understanding Reserve Pay
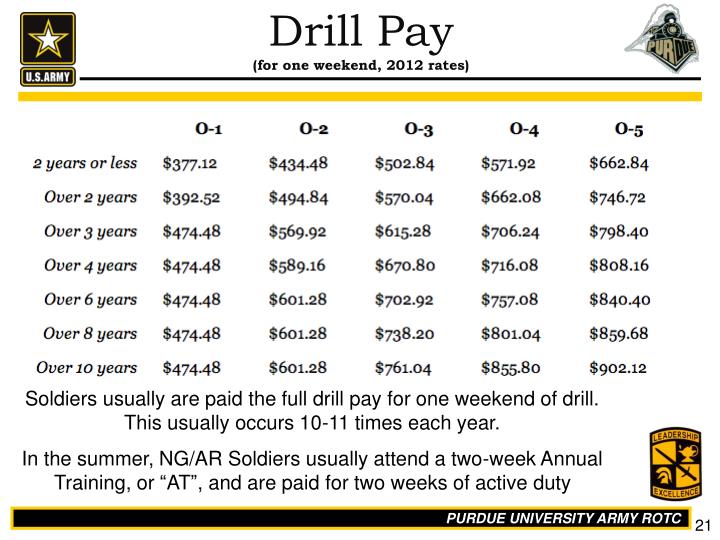
Reserve pay is based on a system known as “drill pay.” This pay scale determines the amount of money a reserve member earns per drill period, which is typically one weekend per month. The pay is calculated based on the member’s rank and the number of years of service. For example, an E-1 (Private) with less than two years of service would earn a certain amount per drill, while an E-5 (Sergeant) with six years of service would earn significantly more.
2024 Reserve Pay Scale
The pay scale for reserves in 2024 will likely mirror the active-duty pay scale, with adjustments for the part-time nature of reserve service. Here’s a breakdown of the estimated monthly drill pay for each rank:
- E-1 (Private): 202.52 - 281.25 per month
- E-2 (Private First Class): 243.48 - 368.49 per month
- E-3 (Specialist/Corporal): 298.43 - 462.57 per month
- E-4 (Sergeant): 354.47 - 609.93 per month
- E-5 (Staff Sergeant): 434.09 - 800.31 per month
- E-6 (Staff Sergeant): 543.19 - 998.55 per month
- E-7 (Sergeant First Class): 674.49 - 1,257.11 per month
- E-8 (Master Sergeant/First Sergeant): 846.39 - 1,629.69 per month
- E-9 (Sergeant Major/Command Sergeant Major): 1,044.59 - 2,046.49 per month
Keep in mind that these figures are estimates and may be subject to change based on legislative actions or other factors.
Benefits of Serving in the Reserves
While the pay for reserves is certainly a consideration, it’s not the only benefit of serving in the military’s part-time force. Here are some of the advantages of joining the reserves:
- Education Benefits: The Montgomery GI Bill Selected Reserve (MGIB-SR) provides education assistance to reserve members, helping to offset the cost of tuition and training.
- Healthcare Benefits: Reserves are eligible for TRICARE, the military’s healthcare program, which provides comprehensive medical, dental, and pharmacy coverage.
- Retirement Benefits: Reserves can earn retirement points, which can be used to calculate their retirement pay and eligibility for benefits like the GI Bill.
- Career Advancement: Serving in the reserves can provide valuable skills and experience, making reserve members more competitive in the civilian job market.
- Travel Opportunities: Reserves may have the chance to travel for training or deployments, exploring new places and experiencing different cultures.
- Camraderie and Esprit de Corps: The bonds formed between reserve members can last a lifetime, providing a sense of belonging and camaraderie.
- Tax Benefits: Reserve members may be eligible for tax benefits like the Armed Forces Tax Credit or the Military Spouse Residency Relief Act.
- Home Loan Guarantees: The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) guarantees home loans for eligible reserve members, making it easier to purchase or refinance a home.
Conclusion
Serving in the reserves is a rewarding and challenging experience that offers a wide range of benefits, from drill pay and education assistance to healthcare and retirement benefits. While the pay may not be the same as active-duty compensation, the advantages of serving in the reserves can be substantial. Whether you’re looking for a way to serve your country, develop new skills, or simply be part of a larger community, the reserves may be the perfect fit.
FAQ Section
How much do reserves get paid per drill period?
+Reserve members earn a certain amount per drill period, based on their rank and years of service. For example, an E-1 with less than two years of service would earn approximately 202.52 per month, while an E-5 with six years of service would earn around 800.31 per month.
What benefits do reserve members receive?
+Reserve members are eligible for a range of benefits, including education assistance, healthcare coverage, retirement benefits, career advancement opportunities, travel, and tax benefits.
How do I join the reserves?
+To join the reserves, you’ll need to meet the eligibility requirements, which typically include being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and meeting the physical and medical standards. You can contact a recruiter or visit the website of the branch you’re interested in joining to learn more.
Can I serve in the reserves while attending college?
+How long do I have to serve in the reserves?
+The length of service in the reserves varies depending on the branch and the type of enlistment. Typically, reserve members serve one weekend per month and two weeks per year, with a minimum service commitment of six years.

