How Does Organic Farming Work? Natural Methods
Organic farming is an agricultural approach that emphasizes the use of natural methods to maintain soil fertility, control pests and diseases, and promote overall ecosystem health. This approach is based on the principle of working in harmony with nature, rather than relying on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. By adopting organic farming practices, farmers can produce high-quality, nutritious food while minimizing the environmental impact of their operations.
The Core Principles of Organic Farming
At its core, organic farming is about creating a balanced and diverse ecosystem that is capable of sustaining itself over time. This is achieved through the implementation of several key principles, including:
- Soil Conservation and Improvement: Organic farmers use techniques such as crop rotation, composting, and cover cropping to maintain soil fertility and structure. This approach helps to build soil organic matter, increase the water-holding capacity of the soil, and support the growth of beneficial microorganisms.
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Organic farms often feature a diverse range of crops and animals, which helps to promote ecosystem services such as pollination, pest control, and climate regulation. By maintaining biodiversity, organic farmers can reduce their reliance on external inputs and create a more resilient and adaptable farming system.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Organic farmers use a range of techniques to manage pests and diseases, including crop rotation, biological control, and cultural controls. This approach helps to minimize the use of synthetic pesticides and maintain ecosystem balance.
- Animal Welfare: Organic farming emphasizes the importance of animal welfare and promotes the use of humane and sustainable animal husbandry practices. This includes providing animals with access to fresh air, water, and pasture, as well as ensuring that they are handled and cared for in a way that minimizes stress and promotes their overall well-being.
Natural Methods Used in Organic Farming
Organic farmers use a range of natural methods to maintain soil fertility, control pests and diseases, and promote ecosystem health. Some of the most common techniques include:
- Composting: Composting involves the breakdown of organic materials such as food waste, manure, and crop residues into a nutrient-rich soil amendment. This approach helps to recycle nutrients, improve soil structure, and support the growth of beneficial microorganisms.
- Crop Rotation: Crop rotation involves the rotation of different crops on the same land to maintain soil fertility, control pests and diseases, and promote ecosystem balance. This approach helps to break disease and pest cycles, improve soil structure, and increase the overall productivity of the farm.
- Biological Control: Biological control involves the use of living organisms such as predators, parasites, and pathogens to manage pests and diseases. This approach helps to minimize the use of synthetic pesticides and maintain ecosystem balance.
- Cover Cropping: Cover cropping involves the use of crops such as legumes, grasses, and cereals to protect and enrich the soil. This approach helps to prevent soil erosion, improve soil fertility, and support the growth of beneficial microorganisms.
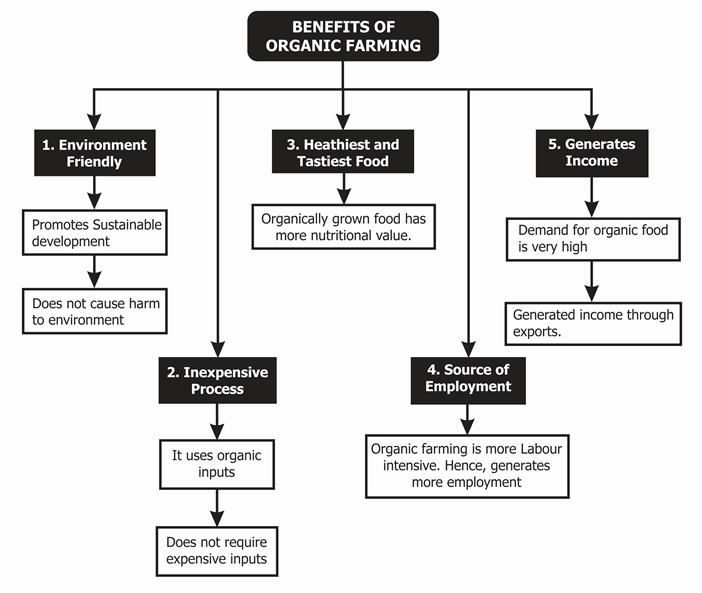
The Benefits of Organic Farming
Organic farming offers a range of benefits for both farmers and the environment. Some of the most significant advantages include:
- Improved Soil Health: Organic farming practices such as composting, cover cropping, and crop rotation help to improve soil fertility, structure, and overall health.
- Increased Biodiversity: Organic farms often feature a diverse range of crops and animals, which helps to promote ecosystem services and maintain ecosystem balance.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Organic farming minimizes the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which helps to reduce the environmental impact of agricultural operations.
- Improved Animal Welfare: Organic farming emphasizes the importance of animal welfare and promotes the use of humane and sustainable animal husbandry practices.
Challenges and Limitations of Organic Farming
While organic farming offers a range of benefits, it also presents several challenges and limitations. Some of the most significant include:
- Higher Labor Requirements: Organic farming often requires more labor than conventional farming, as farmers need to implement techniques such as composting, crop rotation, and biological control.
- Lower Yields: Organic farming can result in lower yields than conventional farming, as farmers may not use synthetic fertilizers and pesticides to maximize production.
- Higher Costs: Organic farming can be more expensive than conventional farming, as farmers need to purchase organic seeds, fertilizers, and other inputs.
Conclusion
Organic farming is a holistic approach to agriculture that emphasizes the use of natural methods to maintain soil fertility, control pests and diseases, and promote ecosystem health. By adopting organic farming practices, farmers can produce high-quality, nutritious food while minimizing the environmental impact of their operations. While organic farming presents several challenges and limitations, it offers a range of benefits for both farmers and the environment, and is an important step towards creating a more sustainable and resilient food system.
What are the core principles of organic farming?
+Organic farming is based on the principles of soil conservation and improvement, biodiversity and ecosystem services, integrated pest management, and animal welfare.
What are some natural methods used in organic farming?
+Organic farmers use a range of natural methods, including composting, crop rotation, biological control, and cover cropping.
What are the benefits of organic farming?
+Organic farming offers several benefits, including improved soil health, increased biodiversity, reduced environmental impact, and improved animal welfare.


