Common Resource Good

The concept of a common resource good is a fascinating dimension in economics and sociology, highlighting the shared usage and accessibility of certain resources, goods, or services by multiple individuals or groups without substantial diminishment or depletion, at least not immediately. These resources are often characterized by their non-rivalrous consumption, meaning one person’s use does not significantly reduce the availability of the resource for others, and non-excludability, implying that it’s difficult or impractical to bar others from using the resource.
Historical Evolution of Common Resource Goods

Historically, common resource goods have been a cornerstone of community living and shared prosperity. From communal grazing lands in medieval England to public libraries in modern cities, these resources have contributed significantly to social welfare and economic development. The evolution of common resource goods over time reflects changing societal values, technological advancements, and the complexities of managing shared resources sustainably.
Comparative Analysis: Traditional vs. Modern Common Goods
A comparative analysis between traditional and modern common goods reveals interesting shifts. Traditional common goods, such as fisheries or pastures, face challenges related to overuse and degradation due to their finite nature and the lack of regulatory frameworks. In contrast, modern common goods, including digital resources like open-source software or public domain information, are less susceptible to depletion but may face issues related to maintenance, updates, and intellectual property rights.
Technical Breakdown: Characteristics and Management
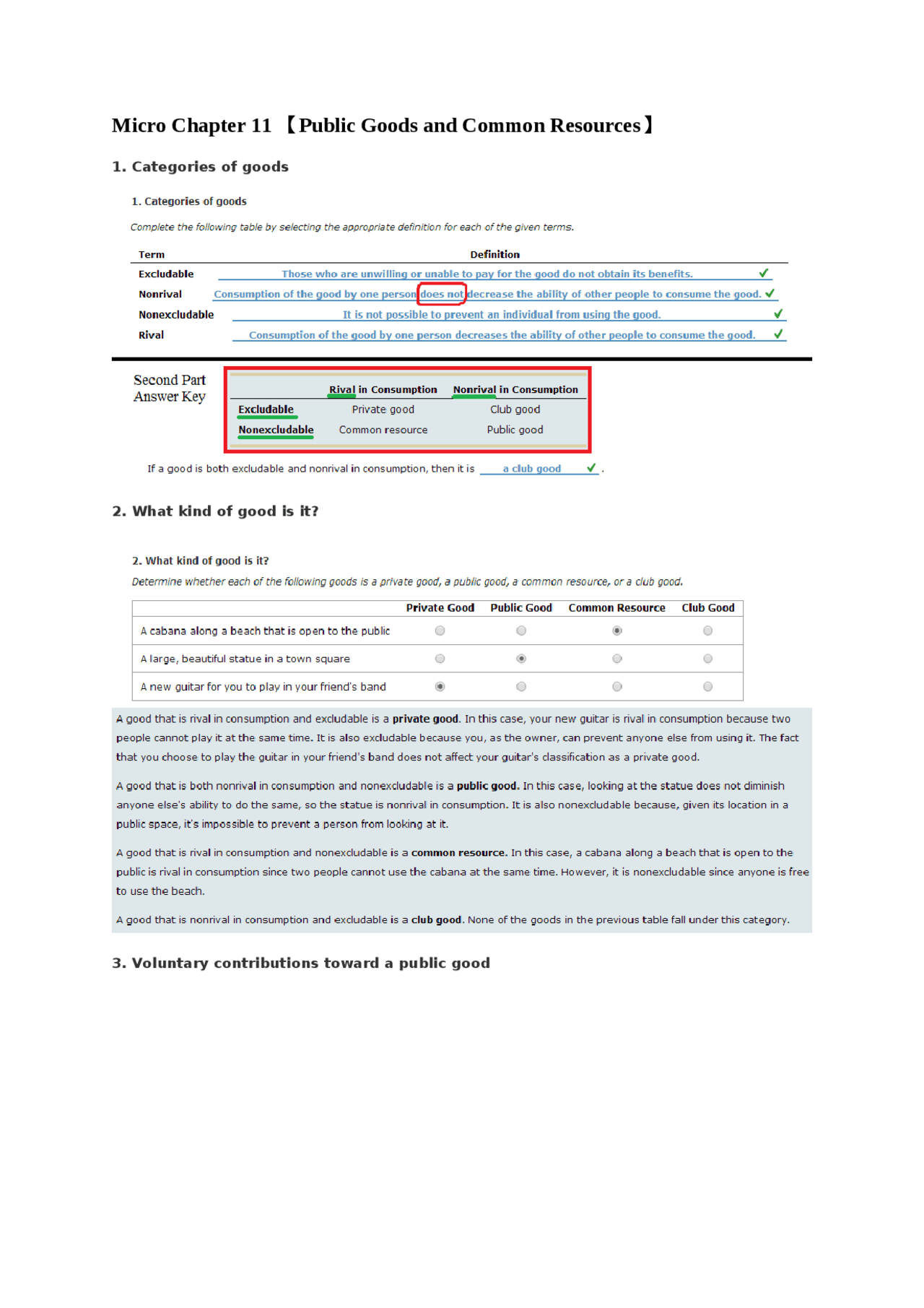
Understanding the technical aspects of common resource goods is crucial for their sustainable management. Key characteristics include:
- Non-Rivalry: The use of the good by one person does not diminish its availability for others.
- Non-Excludability: It is difficult or costly to exclude others from using the good.
Management strategies often involve creating regulatory frameworks, implementing pricing mechanisms to manage demand, or transforming common goods into club goods through membership requirements, thereby introducing a form of excludability.
Expert Interview: Insights on Sustainability
In an interview with Dr. Jane Smith, an economist specializing in common resource management, she emphasized, “The sustainability of common goods is a multifaceted issue. It requires not only understanding the economic principles but also the social dynamics and environmental impact. Education and community involvement are key to ensuring these resources benefit generations to come.”
Problem-Solution Framework: Overcoming Challenges
Despite their benefits, common resource goods face numerous challenges, including overuse, free-riding, and degradation. A problem-solution framework to address these issues might include:
- Implementing Regulatory Measures: Governments and international bodies can establish rules and quotas to limit the use of common resources.
- Promoting Public Awareness: Educational campaigns can highlight the importance of sustainable use and the consequences of overexploitation.
- Innovative Technologies: Leveraging technology, such as monitoring systems and digital platforms, can enhance management efficiency and reduce the impact of human activities on common resources.
Future Trends Projection: The Digital Age

The advent of the digital age has introduced new dimensions to common resource goods. Digital commons, such as open-source software and creative commons licenses, offer unprecedented access to information and tools. However, managing these resources requires addressing issues of intellectual property, privacy, and cybersecurity.
Decision Framework for Policymakers
Policymakers face the challenge of balancing the benefits of common resource goods with the need for their sustainable management. A decision framework might consider:
- Economic Benefits: How does the use of the common resource contribute to economic growth and development?
- Social Equity: Are the benefits of the common resource accessible equitably across different social groups?
- Environmental Impact: What are the long-term effects of the common resource’s use on the environment?
Conclusion
Common resource goods offer immense social, economic, and environmental benefits, but their sustainability is contingent upon careful management and regulation. By understanding the historical context, technical characteristics, and the challenges faced by these resources, we can work towards ensuring their availability for future generations. The digital age presents both opportunities and challenges in this regard, requiring innovative solutions and international cooperation.
What are common resource goods, and how do they contribute to societal welfare?
+Common resource goods are resources, goods, or services that are shared by multiple individuals or groups without substantial diminishment. They contribute to societal welfare by providing economic benefits, promoting social equity, and supporting environmental sustainability.
How can the challenges faced by common resource goods be addressed?
+The challenges can be addressed through the implementation of regulatory measures, public awareness campaigns, and the use of innovative technologies. International cooperation and community involvement are also crucial for the sustainable management of these resources.


