Cats Respiratory Rate Guide
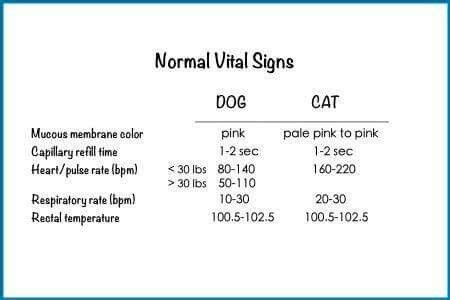
The respiratory rate of a cat is a crucial indicator of its overall health, and as a responsible cat owner or enthusiast, it’s essential to understand what constitutes a normal respiratory rate and how to identify potential issues. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of feline respiratory health, exploring the intricacies of breathing patterns, the factors that influence respiratory rate, and the steps you can take to ensure your feline friend remains healthy and thriving.
Understanding Feline Respiratory Anatomy
Before we dive into the specifics of respiratory rates, it’s essential to understand the basic anatomy of a cat’s respiratory system. The respiratory system consists of the nose, mouth, throat, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Cats, being obligate nasal breathers, primarily breathe through their noses, which are rich in olfactory receptors, allowing them to detect even the subtlest scents. The air then passes through the throat and into the trachea, which splits into the bronchi, eventually leading to the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
What is a Normal Respiratory Rate for Cats?
A normal respiratory rate for cats can vary depending on several factors, including age, size, and activity level. On average, a healthy adult cat breathes between 16 to 40 times per minute. Kittens, due to their smaller lung capacity and higher metabolic rate, may breathe faster, often between 30 to 50 breaths per minute. It’s crucial to remember that these are general guidelines, and the normal respiratory rate can vary slightly from one cat to another.
Factors Influencing Respiratory Rate
Several factors can influence a cat’s respiratory rate, including:
- Age and Size: As mentioned, kittens and smaller cats tend to breathe faster than adult or larger cats.
- Activity Level: Cats that are highly active or have just exercised may breathe more rapidly as their body demands more oxygen.
- Environmental Conditions: Extreme temperatures, humidity, or exposure to pollutants can affect respiratory rate.
- Health Status: Cats with respiratory diseases, heart conditions, or other health issues may exhibit abnormal breathing patterns.
- Emotional State: Stress or anxiety can cause rapid breathing in cats.
Identifying Abnormal Respiratory Rates
Monitoring your cat’s respiratory rate can be an effective way to identify potential health issues early on. An abnormal respiratory rate in cats can be characterized by rates that are significantly higher or lower than the average range. For example:
- Tachypnea: Rapid breathing, often associated with stress, anxiety, or respiratory distress.
- Bradypnea: Slow breathing, which can be a sign of neurological issues, respiratory failure, or other severe health conditions.
How to Measure Your Cat’s Respiratory Rate
Measuring your cat’s respiratory rate can be a straightforward process if done correctly. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Choose a Quiet and Comfortable Environment: Ensure your cat is relaxed and not stressed or excited.
- Watch the Chest Rise and Fall: Count each rise as one breath. You can also place your hand gently on the side of the chest to feel the breaths if visual counting is challenging.
- Count for One Minute: For accuracy, it’s best to count the breaths for a full minute. If your cat is too restless, you can count for 15 seconds and then multiply by 4, but this method may be less accurate.
- Record the Rate: Note down the respiratory rate and the conditions under which it was measured. This can be helpful for future comparisons or for your veterinarian.
Managing Respiratory Health in Cats
Maintaining your cat’s respiratory health is crucial for its overall well-being. Here are some tips to support respiratory health:
- Regular Veterinary Check-Ups: Annual check-ups can help identify respiratory issues early.
- Provide a Clean Environment: Ensure good ventilation and keep your home free from pollutants and allergens.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity can exacerbate respiratory conditions.
- Keep Your Cat Up-to-Date on Preventatives: Regular use of heartworm preventatives and staying current on vaccinations can help protect against diseases that may affect respiratory health.
Conclusion
The respiratory health of your cat is a vital aspect of its overall well-being, and understanding what constitutes a normal respiratory rate, as well as the factors that can influence it, can empower you to provide the best possible care. By being vigilant, maintaining a healthy environment, and seeking regular veterinary care, you can help ensure your feline companion lives a long, healthy life.
What is considered a normal respiratory rate for kittens?
+Kittens, due to their higher metabolic rate and smaller lung capacity, typically breathe faster than adult cats, with a normal range of 30 to 50 breaths per minute.
How often should I measure my cat’s respiratory rate?
+It’s a good idea to occasionally measure your cat’s respiratory rate when they are relaxed to establish a baseline. This can help you identify any changes or abnormalities more easily.
What are some signs of respiratory distress in cats?
+Signs of respiratory distress in cats can include rapid or labored breathing, panting, blue-tinged gums or lips, and difficulty breathing. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek veterinary attention immediately.