Bottom Foot Tendons
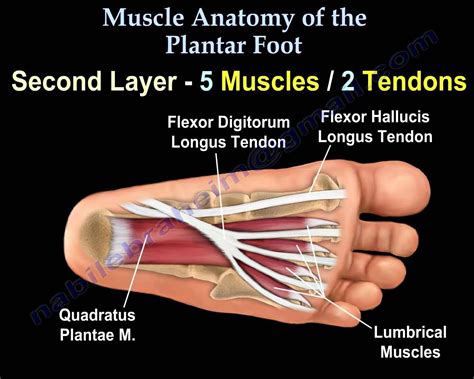
The bottom foot tendons, comprising the posterior tibial tendon, the peroneal tendons, and the flexor tendons, play a crucial role in maintaining the foot’s arch, facilitating movement, and supporting the body’s weight. These tendons, along with the muscles they are attached to, are essential for walking, running, and other physical activities. However, they are also susceptible to injuries and conditions that can lead to pain and disability.
One of the most common issues affecting the bottom foot tendons is posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD). This condition occurs when the posterior tibial tendon, which runs along the inner side of the ankle and supports the foot’s arch, becomes inflamed or torn. PTTD can cause pain, swelling, and flattening of the foot, making it difficult to walk or stand for extended periods.
Understanding the Anatomy
To appreciate the importance of the bottom foot tendons, it is essential to understand their anatomy. The posterior tibial tendon originates from the posterior tibial muscle in the lower leg and inserts into the navicular and cuneiform bones in the foot. This tendon plays a vital role in supporting the foot’s arch and enabling the foot to move inward, a motion known as inversion.
The peroneal tendons, on the other hand, are located on the outer side of the ankle and are responsible for foot eversion, which is the movement of the foot outward. These tendons also help to stabilize the ankle joint and prevent excessive rolling or twisting.
The flexor tendons, comprising the flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus, are situated on the bottom of the foot and are involved in toe flexion. These tendons enable the toes to curl downward and are essential for balance and push-off during gait.
Common Issues and Injuries
In addition to PTTD, other common issues and injuries affecting the bottom foot tendons include:
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons, often caused by overuse or repetitive strain.
- Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendons, which can lead to chronic pain and weakness.
- Tears: Partial or complete ruptures of the tendons, which can be traumatic or degenerative in nature.
- Peroneal tendon dislocation: Displacement of the peroneal tendons out of their normal position, which can cause pain and instability.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing issues with the bottom foot tendons typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies, and medical history. A healthcare professional may perform tests such as the “too many toes” sign, where the patient is asked to stand on their toes to assess the foot’s arch, or the “single heel raise” test, which evaluates the strength of the posterior tibial tendon.
Treatment for bottom foot tendon issues depends on the severity and nature of the condition. Conservative management may include:
- Rest and ice: Avoiding activities that exacerbate the condition and applying ice to reduce inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Exercises and stretches to improve flexibility and strength.
- Orthotics and shoe modifications: Using supportive devices or altering footwear to reduce stress on the tendons.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications or pain relievers to manage symptoms.
In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair or reconstruct the damaged tendons.
Prevention and Maintenance
Preventing issues with the bottom foot tendons requires a combination of proper footwear, regular exercise, and good foot care. Some tips include:
- Wearing supportive shoes: Shoes with good arch support and cushioning can help reduce stress on the tendons.
- Stretching and strengthening: Regular exercises to improve flexibility and strength in the foot and ankle.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can put additional stress on the tendons, increasing the risk of injury.
- Avoiding overuse: Gradually increasing physical activity to avoid putting excessive strain on the tendons.
What are the symptoms of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction?
+Symptoms of PTTD may include pain and swelling on the inner side of the ankle, flattening of the foot, and difficulty walking or standing for extended periods.
How can I prevent issues with my bottom foot tendons?
+To prevent issues with your bottom foot tendons, wear supportive shoes, stretch and strengthen your feet and ankles regularly, maintain a healthy weight, and avoid overuse.
What is the treatment for peroneal tendon dislocation?
+Treatment for peroneal tendon dislocation may include bracing, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical intervention to repair or reconstruct the damaged tendons.
In conclusion, the bottom foot tendons play a vital role in maintaining foot function and supporting the body’s weight. Understanding the anatomy, common issues, and injuries affecting these tendons is essential for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. By taking preventative measures and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can reduce their risk of developing issues with their bottom foot tendons and maintain optimal foot health.

