8 Lifespan Stages To Understand Human Growth
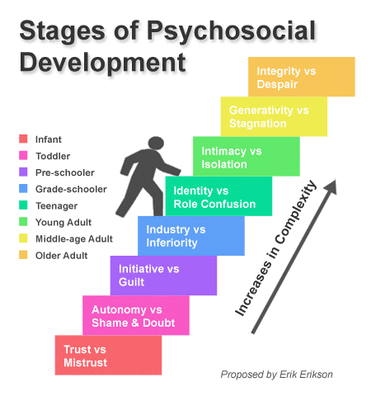
Human development is a complex and multifaceted process that spans an entire lifetime. Understanding the various stages of human growth can provide valuable insights into the psychological, physical, and emotional changes that individuals undergo as they mature. The concept of lifespan stages suggests that human development is divided into distinct phases, each characterized by specific milestones, challenges, and opportunities for growth. In this article, we will explore eight key lifespan stages that are essential to understanding human development.
Stage 1: Infancy (0-1 year)
Infancy is the first stage of human development, spanning from birth to approximately one year of age. During this period, infants undergo rapid physical growth and development, including the formation of vital organs, the development of sensory perception, and the emergence of basic motor skills. Infants are entirely dependent on their caregivers for survival, and their primary mechanism for communication is crying. As infants begin to explore their environment, they start to develop trust with their caregivers, which lays the foundation for future relationships and attachment styles.
Stage 2: Toddlerhood (1-3 years)
Toddlerhood is a critical stage of development that occurs between the ages of one and three. During this period, children experience rapid cognitive, emotional, and physical growth. They begin to assert their independence, exploring their surroundings and testing boundaries. Toddlers also start to develop language skills, learning to communicate through simple words and phrases. This stage is marked by the emergence of tantrums, which are a normal part of cognitive and emotional development. Caregivers play a vital role in shaping toddlers’ behavior, teaching them essential skills like sharing, empathy, and self-regulation.
Stage 3: Early Childhood (4-6 years)
Early childhood is a stage of significant growth and development, spanning from approximately four to six years of age. During this period, children continue to refine their language skills, learning to communicate more effectively and express their thoughts and feelings. They also begin to develop social skills, learning to interact with peers and form friendships. Early childhood is a critical time for cognitive development, as children start to develop problem-solving skills, learn to categorize objects, and demonstrate an understanding of cause-and-effect relationships.
Stage 4: Middle Childhood (7-10 years)
Middle childhood is a stage of development that occurs between the ages of seven and ten. During this period, children experience significant cognitive and social growth. They develop more complex problem-solving skills, learn to think critically, and demonstrate a greater understanding of abstract concepts. Middle childhood is also marked by the emergence of friendships and social relationships, as children learn to navigate peer groups and develop a sense of belonging. This stage is critical for developing emotional intelligence, as children learn to recognize, understand, and manage their emotions.
Stage 5: Late Childhood (11-14 years)
Late childhood is a stage of development that spans from approximately eleven to fourteen years of age. During this period, children undergo significant physical, emotional, and cognitive changes. They experience the onset of puberty, which brings about rapid physical growth and the emergence of secondary sex characteristics. Late childhood is also marked by the development of more complex social relationships, as children learn to navigate adolescence and form closer bonds with peers. This stage is critical for developing identity, as children begin to explore their interests, values, and beliefs.
Stage 6: Adolescence (15-19 years)
Adolescence is a stage of development that occurs between the ages of fifteen and nineteen. During this period, individuals undergo significant physical, emotional, and cognitive changes. They experience the completion of puberty, which brings about final physical growth and the emergence of adult physical characteristics. Adolescence is marked by the development of more complex social relationships, as individuals learn to navigate romantic relationships, form close bonds with peers, and develop a sense of identity. This stage is critical for developing autonomy, as individuals begin to assert their independence and make decisions that shape their future.
Stage 7: Young Adulthood (20-39 years)
Young adulthood is a stage of development that spans from approximately twenty to thirty-nine years of age. During this period, individuals experience significant cognitive, emotional, and social growth. They develop more complex problem-solving skills, learn to think critically, and demonstrate a greater understanding of abstract concepts. Young adulthood is marked by the emergence of career goals, as individuals begin to explore their professional interests and develop a sense of purpose. This stage is critical for developing intimacy, as individuals form close relationships with romantic partners, friends, and family members.
Stage 8: Middle Adulthood (40-64 years)
Middle adulthood is a stage of development that occurs between the ages of forty and sixty-four. During this period, individuals experience significant cognitive, emotional, and social changes. They develop more complex problem-solving skills, learn to think critically, and demonstrate a greater understanding of abstract concepts. Middle adulthood is marked by the emergence of generativity, as individuals begin to focus on giving back to their communities and leaving a lasting legacy. This stage is critical for developing a sense of reflection, as individuals begin to evaluate their life choices, reconcile past experiences, and develop a greater understanding of themselves and their place in the world.
FAQ Section
What are the most critical factors that influence human development across the lifespan?
+The most critical factors that influence human development across the lifespan include genetics, environment, culture, socioeconomic status, and access to education and healthcare. These factors can have a profound impact on cognitive, emotional, and physical development, shaping the course of an individual's life and influencing their overall well-being.
How do lifespan stages impact our understanding of human development?
+Lifespan stages provide a framework for understanding the complex and dynamic process of human development. By recognizing the unique characteristics, challenges, and opportunities of each stage, we can better appreciate the intricate interplay between biological, psychological, and social factors that shape human growth and development.
What role do caregivers play in shaping human development during the early lifespan stages?
+Caregivers play a vital role in shaping human development during the early lifespan stages. They provide essential care, support, and guidance, teaching children important skills like trust, empathy, and self-regulation. Caregivers also serve as role models, influencing children's social, emotional, and cognitive development and shaping their understanding of the world.
How do social relationships impact human development across the lifespan?
+Social relationships play a critical role in human development across the lifespan. They provide emotional support, a sense of belonging, and opportunities for socialization, influencing cognitive, emotional, and physical development. Social relationships can also serve as a source of stress, conflict, and adversity, highlighting the importance of developing healthy relationship skills and maintaining a strong support network.
What are some key strategies for promoting healthy development across the lifespan?
+Key strategies for promoting healthy development across the lifespan include providing a nurturing environment, fostering social connections, encouraging physical activity, promoting cognitive stimulation, and teaching emotional regulation skills. Additionally, accessing education and healthcare, developing a growth mindset, and cultivating a sense of purpose and meaning can also support healthy development and overall well-being.
In conclusion, the eight lifespan stages provide a comprehensive framework for understanding human growth and development. By recognizing the unique characteristics, challenges, and opportunities of each stage, we can better appreciate the complex and dynamic process of human development and develop strategies for promoting healthy growth and well-being across the lifespan.
