12 Pqrst Assessment Tips For Effective Pain Management
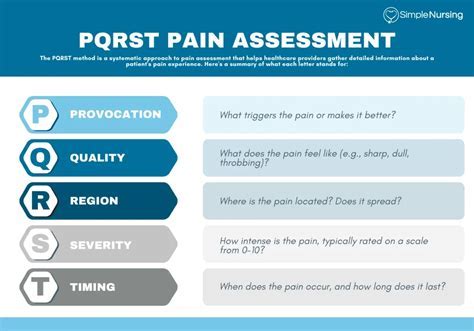
Effective pain management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that can significantly impact the quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic or acute pain. One approach to assessing pain and guiding its management is the PQRST assessment method. This acronym stands for Pain, Quality, Region, Severity, and Time, and sometimes additional factors such as Trigger and Relief. Understanding and applying the PQRST assessment tips can help healthcare providers offer more personalized and effective care. Here’s a breakdown of the PQRST method with additional insights into effective pain management:
P - Pain
- Description and Characterization: The first step in the PQRST method involves describing the pain. This includes asking the patient to characterize their pain as sharp, dull, aching, burning, etc. Understanding the nature of the pain can provide clues about its origin and the most effective treatment strategies.
Q - Quality
- Sensory Details: The quality of pain refers to its descriptive characteristics, such as throbbing, stabbing, or cramping. This aspect helps in differentiating between various types of pain (e.g., nociceptive vs. neuropathic) and can guide the selection of appropriate pharmacological or non-pharmacological interventions.
R - Region
- Location and Radiation: Identifying the location of the pain and whether it radiates to other areas is crucial. This can help in identifying the source of pain. For example, pain radiating down the arm from the neck might suggest a cervical spine issue, while pain radiating down the leg could indicate a lumbar spine problem.
S - Severity
- Quantification: Assessing the severity of pain is typically done using a pain scale, where patients rate their pain from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain). This quantification helps in monitoring the effectiveness of treatments over time and in making informed decisions about the need for adjustments in the treatment plan.
T - Time
- Onset, Duration, and Patterns: Understanding when the pain started, how long it lasts, and whether it follows any patterns (e.g., worse in the morning, improves with movement) can provide valuable information. This temporal aspect of pain can help in diagnosing the underlying cause and in planning interventions that take into account the patient’s daily activities and schedule.
Additional Considerations
- Trigger: Identifying what triggers the pain or makes it worse can help in devising strategies to avoid or mitigate these factors. This could involve lifestyle changes, ergonomic adjustments, or learning specific exercises to strengthen supportive muscles.
- Relief: Understanding what provides relief can offer clues about the nature of the pain and guide treatment decisions. For example, if rest provides significant relief, this might suggest an inflammatory or mechanical component to the pain.
Effective Pain Management Strategies
- Multimodal Approach: Often, the most effective pain management strategies involve a combination of pharmacological (e.g., NSAIDs, opioids, neuropathic pain agents), non-pharmacological (e.g., physical therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy), and interventional (e.g., injections, nerve blocks) treatments.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about their pain, its management, and the importance of adherence to treatment plans can improve outcomes. This includes discussing the risks and benefits of different treatments and involving patients in decision-making.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Encouraging lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, weight management, smoking cessation, and stress reduction techniques (e.g., meditation, deep breathing) can also play a crucial role in managing pain.
- Interdisciplinary Care: Collaborative care that involves different healthcare professionals (e.g., physicians, physical therapists, psychologists) can provide comprehensive support and address the multifaceted nature of pain.
- Regular Follow-Up: Regular assessments and follow-ups are essential to adjust treatment plans as necessary and to ensure that the patient’s needs are being met effectively.
Conclusion
Effective pain management is a complex process that requires a thoughtful and individualized approach. By applying the PQRST assessment method and considering additional factors such as trigger and relief, healthcare providers can develop a deeper understanding of their patients’ experiences and design more effective treatment plans. Remember, the goal of pain management is not only to reduce pain but also to improve function and quality of life.
What is the PQRST method in pain assessment?
+The PQRST method is a systematic approach to assessing pain, standing for Pain, Quality, Region, Severity, and Time, and sometimes including Trigger and Relief. It helps healthcare providers gather detailed information about a patient's pain to guide effective management.
Why is it important to assess the severity of pain?
+Assessing the severity of pain is crucial for monitoring the effectiveness of treatments and making informed decisions about adjustments in the treatment plan. It also helps in understanding the patient's current state and in setting realistic goals for pain management.
What role does patient education play in pain management?
+Patient education is vital in pain management as it empowers patients with the knowledge to understand their condition, the risks and benefits of different treatments, and the importance of adherence to treatment plans. Educated patients are more likely to be active participants in their care, leading to better outcomes.
By following the PQRST assessment tips and incorporating a comprehensive approach to pain management, healthcare providers can offer more tailored and effective care, ultimately improving the lives of individuals suffering from pain.