12 Lewis Dot Structure Tips For Ocn Mastery
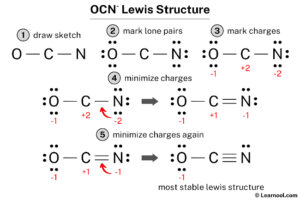
Mastering Lewis dot structures is a fundamental aspect of understanding chemistry, particularly in the context of organic and inorganic compounds. The ability to accurately depict the distribution of electrons within a molecule is crucial for predicting its reactivity, polarity, and other significant properties. Here are 12 tailored tips to achieve mastery over Lewis dot structures, focusing on the specifics of understanding and applying these structures with precision.
1. Understand the Basics of Lewis Dot Structures
Start by grasping the fundamental concept that Lewis dot structures represent the valence electrons of atoms within a molecule. Each atom is symbolized by its elemental symbol, and valence electrons are represented as dots around the symbol. Understanding how atoms share these electrons to form bonds is key.
2. Know the Octet Rule
Most atoms aim to have eight electrons in their outer shell, similar to the noble gas configuration, which is highly stable. This guideline, known as the octet rule, helps in predicting how many bonds an atom can form. However, it’s essential to remember that not all atoms follow this rule, especially in the cases of hydrogen, which needs only two electrons, and some atoms that can expand their octet.
3. Determine the Total Valence Electrons
To draw a Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons in the molecule by summing the valence electrons of each atom and then adjusting for any charge on the molecule. This total is crucial for ensuring that your Lewis structure accurately represents the molecule’s electron distribution.
4. Connect Atoms with Single Bonds
Begin by connecting atoms with single bonds, which represent two shared electrons. The arrangement should resemble the molecular formula’s skeletal structure, keeping in mind that some atoms, like hydrogen, can only form one bond.
5. Satisfy the Octet Rule for Each Atom
After forming single bonds, distribute the remaining electrons to satisfy the octet rule for each atom, if possible. This step may involve forming double or triple bonds between atoms that can accommodate more than eight electrons in their valence shell.
6. Consider Formal Charges
When constructing Lewis structures, it’s vital to consider formal charges on atoms. The formal charge is calculated by subtracting the number of non-bonding electrons and half the number of bonding electrons from the atom’s valence electrons. Structures with lower formal charges are generally more stable.
7. Resonance Structures
For molecules that can have multiple bonding arrangements (resonance structures), it’s essential to draw all possible structures and understand that the actual molecule is a hybrid of these. Resonance is key to understanding the behavior of many organic and inorganic compounds.
8. Expandable Octets
Be aware of atoms, especially those in period 3 and below of the periodic table, that can expand their octet. This ability is crucial for understanding the structures of compounds like SF6, where sulfur forms six bonds.
9. Lewis Structures for Ions
When drawing Lewis structures for ions, adjust the total valence electron count based on the charge. For cations, subtract electrons, and for anions, add electrons. This adjustment is critical for accurately depicting the electron distribution in ionic species.
10. Practice with Simple Molecules
Start with simple molecules like H2O, CO2, and CH4 to hone your skills. Gradually move to more complex molecules, incorporating the rules and exceptions you’ve learned.
11. Utilize Online Tools and Resources
Several online tools and software can help you practice drawing Lewis structures and check your work for accuracy. These resources can be invaluable for reinforcing your understanding and catching mistakes.
12. Apply to Real-World Compounds
Finally, apply your skills to real-world compounds, analyzing how the Lewis structure influences the chemical properties and reactivity of the molecule. This step helps in consolidating your knowledge and making it more applicable to real chemical problems.
FAQ Section
What is the significance of drawing Lewis structures in chemistry?
+Drawing Lewis structures is crucial for understanding the distribution of electrons within a molecule, which in turn helps predict the molecule's reactivity, polarity, and other significant chemical properties.
How do you determine the total number of valence electrons in a molecule?
+The total number of valence electrons is determined by summing the valence electrons of each atom in the molecule and then adjusting for any charge on the molecule.
What is the purpose of considering formal charges in Lewis structures?
+Formal charges help in evaluating the stability of a Lewis structure. Structures with lower formal charges are generally more stable and preferred.
By following these tips and practicing regularly, you’ll not only master Lewis dot structures but also deepen your understanding of chemistry and improve your ability to analyze and predict molecular behavior. Remember, practice and application are key to becoming proficient in drawing and interpreting Lewis structures.