10 Coughing Causes Stomach Pain Explained
Coughing is a natural reflex that helps clear the airways of irritants, but it can sometimes lead to discomfort in other parts of the body, including the stomach. When coughing causes stomach pain, it can be alarming and puzzling. Understanding the possible reasons behind this phenomenon can help alleviate concerns and guide appropriate management. Here are ten potential explanations for why coughing might cause stomach pain, explored in depth to provide a comprehensive overview of this issue.
1. Increased Abdominal Pressure
Coughing involves the sudden, forceful expulsion of air from the lungs, which increases pressure within the abdominal cavity. This increased pressure can put strain on the stomach and surrounding muscles, potentially leading to discomfort or pain. Individuals with pre-existing abdominal issues, such as hernias or previous surgeries, might be more susceptible to this kind of pain due to the additional pressure.
2. Irritation of the Diaphragm
The diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdomen, plays a crucial role in breathing and coughing. When you cough, the diaphragm contracts and relaxes rapidly. If the diaphragm becomes irritated or inflamed, either from frequent or severe coughing, it can cause pain that is felt in the upper abdomen. This pain can be sharp and may worsen with deep breathing or coughing.
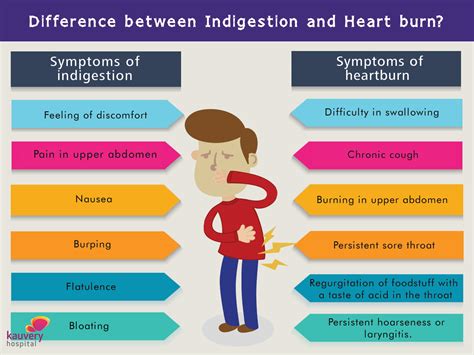
3. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Coughing can exacerbate symptoms of GERD, a condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the tube connecting your mouth and stomach (esophagus). This backwash (acid reflux) can irritate the lining of your esophagus, causing discomfort in the chest and upper abdomen. If you have GERD, coughing can increase the pressure that causes stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus, leading to heartburn and stomach pain.
4. Strain on Abdominal Muscles
Prolonged or intense coughing can strain the abdominal muscles, leading to muscle soreness similar to what you might experience after strenuous exercise. This strain can cause pain or discomfort, especially if the muscles are not accustomed to such activity. The pain is usually dull and can be felt across the abdomen.
5. Stomach Ulcers or Gastritis
In individuals with stomach ulcers or gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining), coughing can increase abdominal pressure and potentially irritate these conditions further. The increased pressure and movement can exacerbate the irritation of the stomach lining, leading to more significant discomfort or pain.
6. Food or Eating Habits
Sometimes, the timing of coughing in relation to eating can contribute to stomach pain. Eating too quickly, not chewing food properly, or consuming foods that are difficult to digest can lead to discomfort. If coughing occurs after eating, it might force food back up into the esophagus, causing irritation and pain, especially if the food is acidic or spicy.
7. Anxiety or Stress
Coughing can be a source of anxiety or stress, especially if it is persistent or severe. This stress can lead to tension in the abdominal muscles, causing pain or discomfort. Additionally, stress can exacerbate existing gastrointestinal issues, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), leading to stomach pain.
8. Underlying Respiratory Conditions
Certain respiratory conditions, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, or asthma, can cause coughing that leads to stomach pain due to the intense and frequent coughing spasms. The body’s response to these conditions, including fever, fatigue, and changes in appetite, can also contribute to abdominal discomfort.
9. Medication Side Effects
Some medications used to treat coughs or respiratory conditions can have side effects that include stomach upset or pain. For example, certain antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs can irritate the stomach lining or cause gastrointestinal upset.
10. Other Systemic Conditions
In rare cases, coughing that leads to stomach pain might be indicative of a more systemic condition that affects multiple body systems. For instance, conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can cause widespread inflammation that might result in both respiratory symptoms (like coughing) and abdominal pain.
Managing Cough-Induced Stomach Pain
While it’s essential to address the underlying cause of the cough, there are several strategies to help manage stomach pain associated with coughing: - Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help thin out mucus, making it easier to cough up, and keep the stomach lining healthy. - Eat Small Meals: Smaller, more frequent meals can reduce symptoms of GERD and put less strain on the stomach. - Choose Gentle Foods: Opt for bland, easily digestible foods to minimize stomach irritation. - Avoid Irritants: If you have GERD or gastritis, avoid foods and drinks that can trigger reflux or irritation. - Practice Good Coughing Hygiene: Cover your mouth when you cough and wash your hands frequently to prevent the spread of infections. - Consider Over-the-Counter Medications: Depending on the cause of your cough and stomach pain, over-the-counter medications like antacids for heartburn or cough suppressants might provide relief. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
If your stomach pain persists, worsens, or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms like difficulty breathing, chest pain, severe vomiting, or blood in your stool or cough, seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your specific condition, ensuring that both your cough and stomach pain are adequately addressed.
What are the most common reasons for stomach pain after coughing?
+The most common reasons include increased abdominal pressure, irritation of the diaphragm, and exacerbation of conditions like GERD or gastritis. Strain on abdominal muscles and the timing of coughing in relation to eating can also contribute to discomfort.
How can I manage stomach pain associated with coughing?
+Staying hydrated, eating small meals, choosing gentle foods, avoiding irritants, practicing good coughing hygiene, and considering over-the-counter medications for symptom relief can help. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
When should I seek medical attention for cough-induced stomach pain?
+You should seek medical attention if your stomach pain persists, worsens, or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms like difficulty breathing, chest pain, severe vomiting, or blood in your stool or cough. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
In conclusion, coughing that causes stomach pain can be due to a variety of reasons, ranging from mechanical factors like increased abdominal pressure to underlying health conditions. By understanding these causes and taking appropriate steps to manage both the cough and the stomach pain, individuals can find relief and improve their overall well-being. Remember, if symptoms persist or worsen, seeking professional medical advice is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.

