1 Knot To Mph
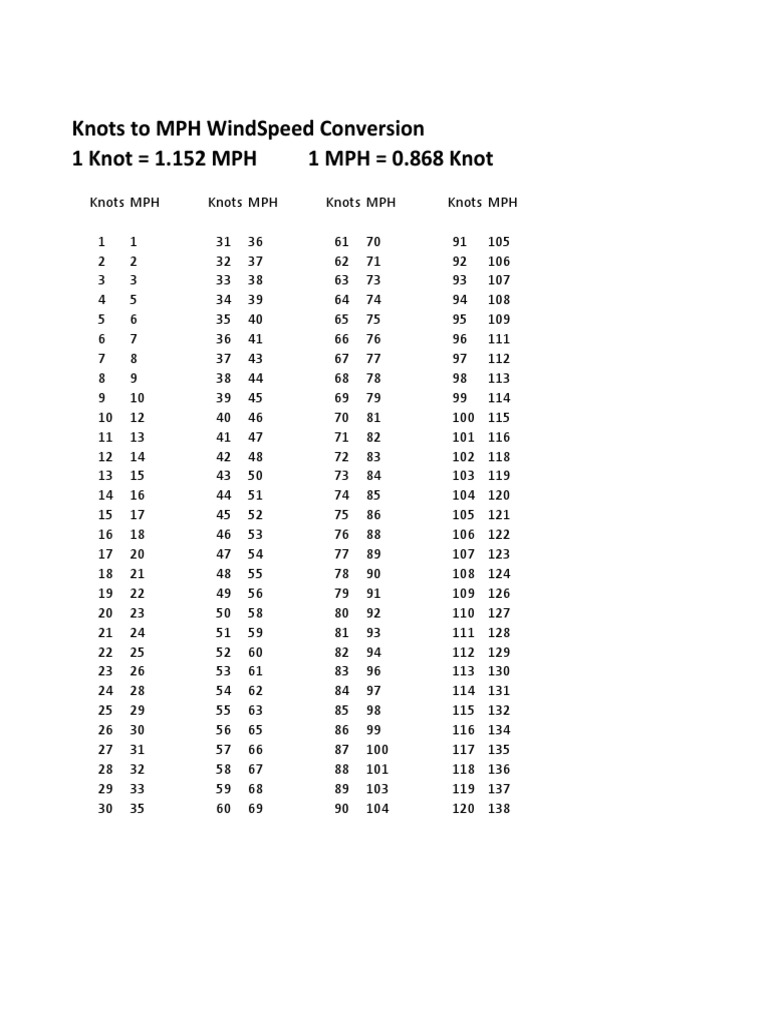
Understanding the conversion between knots and miles per hour (mph) is essential for various fields, including navigation, aviation, and meteorology. In this explanation, we will delve into the process of converting 1 knot to mph, exploring the underlying principles and applications of this conversion.
Introduction to Knots and Miles Per Hour
Knots: A knot is a unit of speed, primarily used in navigation and meteorology. It is defined as one nautical mile per hour. The nautical mile is approximately 6,076.1 feet or 1,852 meters. The use of knots in navigation originated from the practice of measuring a ship’s speed by throwing a knotted rope over the side of the vessel. The number of knots that passed over the side in a given time indicated the ship’s speed.
Miles Per Hour (mph): Miles per hour is a unit of speed based on the imperial system of units. It represents the distance of one mile (5,280 feet or 1,609.34 meters) traveled in one hour. mph is commonly used in everyday applications, such as measuring the speed of vehicles or the wind.
Conversion Process
To convert 1 knot to mph, we must understand the relationship between the nautical mile and the standard mile. Given that 1 nautical mile equals 1,852 meters and 1 standard mile equals 1,609.34 meters, the conversion factor can be derived as follows:
1 nautical mile = 1,852 meters 1 standard mile = 1,609.34 meters
Thus, to find how many standard miles are in a nautical mile:
1 nautical mile = 1,852 meters / 1,609.34 meters/standard mile ≈ 1.15078 standard miles
Since 1 knot = 1 nautical mile per hour, we can convert 1 knot to mph by multiplying by this conversion factor:
1 knot = 1 nautical mile/hour ≈ 1.15078 standard miles/hour
Therefore, 1 knot is approximately equal to 1.15078 mph.
Practical Applications
The conversion between knots and mph is crucial in various contexts:
Aviation: Pilots often need to understand their speed in both knots (for navigation and air traffic control communications) and mph (for general understanding or when communicating with non-aviation entities).
Maritime: The primary speed unit in maritime is the knot, due to its historical roots and the fact that nautical miles are used for charting and navigation purposes.
Meteorology: Wind speeds are often reported in knots for operational and navigation purposes but may also be converted to mph for public weather forecasts to better align with everyday experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, converting 1 knot to mph involves understanding the definitions of both units and the conversion factor between nautical miles and standard miles. This conversion is vital for navigation, aviation, and other fields where precise speed measurements are critical. By grasping this fundamental conversion, individuals can better navigate through different systems of measurement, facilitating clearer communication and more accurate calculations across various disciplines.
What is the primary reason knots are used in navigation?
+Knots are used in navigation primarily because they originated from a historical method of measuring ship speed and have remained as a standard unit due to the use of nautical miles in charting and navigation.
How do pilots benefit from knowing the conversion between knots and mph?
+Pilots benefit from knowing this conversion because it allows them to communicate effectively with both aviation and non-aviation entities, ensuring clear understanding of speed, which is critical for safety and operational purposes.
Why is it essential to convert between knots and mph in meteorology?
+Converting between knots and mph in meteorology is essential for providing weather forecasts that are understandable to the general public while maintaining the precision required for operational and navigation purposes.
By mastering the conversion between knots and mph, individuals can enhance their navigational skills, improve communication across different disciplines, and ensure accuracy in speed measurements, contributing to safer and more efficient operations in various fields.